Today in Russia, inverter technologies are increasingly used in domestic air conditioners, semi-industrial and industrial climate control systems.
Manufacturers claim they win in terms of energy efficiency, performance, room temperature set-up speed and other performance metrics. It is useful for the user to know the principle of operation of such equipment, the differences between inverter air conditioners and conventional ones, the advantages and disadvantages of systems.
Content
- The main design differences between traditional and inverter air conditioners
- The difference in the principles of operation of classic and inverter air conditioners
- Differences in performance between non-inverter and inverter air conditioners
- energy efficiency
- Noise level
- Climate indicators
- Reliability
- Functionality
- Often asked
- Video review comparing inverter and non-inverter air conditioners
The main design differences between traditional and inverter air conditioners
The air conditioner includes:
- A compressor that compresses freon and pumps it through the system lines (in split systems it is located in the outdoor unit).
- A condenser is a device in which the heated refrigerant cools and passes into a liquid state (condenses), giving off the heat taken out of the room into the air (outdoor unit).
- An evaporator in which the cooled liquid freon heats up and evaporates, taking heat from the air (split system indoor unit)
- A fan responsible for blowing air over the evaporator and supplying cooled air to the serviced room (indoor unit).
- A fan that provides forced cooling of the condenser by air flow (outdoor unit).
- Pipelines for pumping refrigerant.
- Filters, air flow distributors (blinds, vertical and horizontal).
- Electronic blocks of control systems.
This structure is used in both classic and inverter air conditioners. The main difference between their designs is the control of the units. So, a conventional air conditioner uses, as a rule, an AC compressor, which is powered by the mains through relay contacts. It is signaled to turn the compressor on and off.
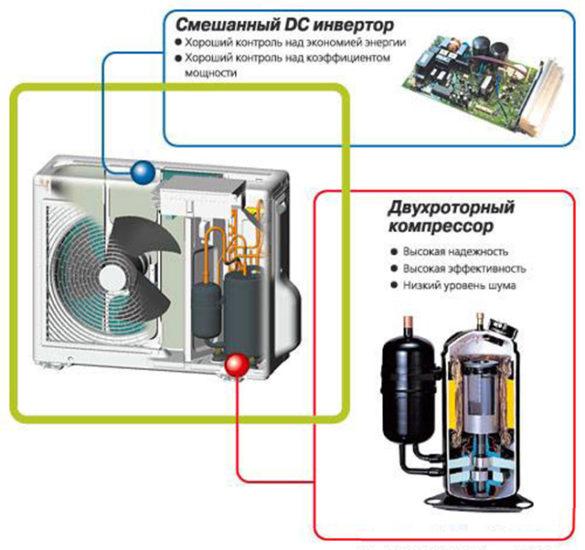 In inverter air conditioners, the power and control of the compressor are organized as follows:
In inverter air conditioners, the power and control of the compressor are organized as follows:
- When installing AC compressors - through a rectifier (converts the AC mains voltage to DC) and an inverter (converts the rectifier's DC voltage to AC with adjustable value and frequency to control speed and power).
- When installing DC compressors - through an inverter that provides output of a unipolar pulsed voltage (DC-Invertor). In this case, to control the speed and power of the compressor, the frequency or pulse width is regulated, depending on the choice of the type of modulation.
Accordingly, the electronic control unit of the inverter air conditioner is more complicated - semiconductor keys of the inverter and its control system are added to it, as a rule, based on a specialized controller.
Full DC-Invertor systems use fans with DC motors. They also receive power from a DC inverter, which allows you to smoothly adjust the rotation speed over a wide range.
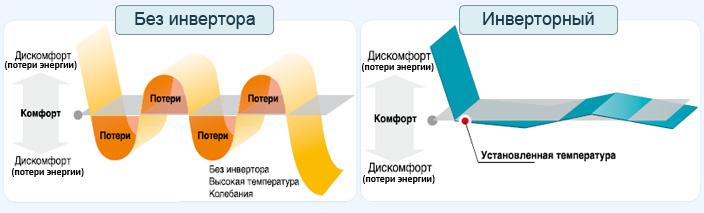
The difference in the principles of operation of classic and inverter air conditioners
In classical climatic installations (non-inverter) the principle of work which received the name "On/Off" is used.
When implemented, the cycle of the air conditioner is as follows:
- When turned on, the compressor reaches full power, pumps the refrigerant through the lines, through the condenser and evaporator.
- As a result, cooled air is blown into the serviced volume until the temperature reaches the limit set in the task (measured by sensors at the inlet of the indoor unit and in the room).
- When the set value is reached, the compressor is switched off, the refrigerant circulation in the circuit stops.
- When the air is heated, based on the signals from the sensors, a switch-on command is again generated, the compressor starts and the cycle repeats.
The operation of any inverter air conditioner is organized differently:
- When starting, the compressor operates at maximum power (often more than nominal) providing rapid cooling / heating of the air in the room.
- When the required temperature is reached, the control system switches the unit to low power mode, necessary and sufficient to maintain the climate parameters in the room with a given accuracy (compensation of small deviations).
- The compressor capacity increases only when the temperature fluctuates significantly or when the setpoint changes.
- Further, the power decreases again, the compressor remains in this mode.
Differences in performance between non-inverter and inverter air conditioners
The difference in operating modes of conventional and inverter air conditioners also affects the differences in performance.
energy efficiency
The “On / Off” mode of a non-inverter air conditioner is characterized by:
- The presence of starting currents, which can exceed the nominal value for the compressor several times.
- The operation of the compressor after start-up in the mode of maximum (usually excess) performance (power).
- Additional energy costs to equalize the pressure in the system after start-up (up to 50% of the refrigerant charge is required in the line).
In an inverter air conditioner:
- A compressor soft start system has been implemented, which makes it possible to reduce starting currents.
- There is no need for pressure equalization as the compressor does not stop.
- In the operating mode, the minimum power is consumed, sufficient to maintain the temperature at a given level with a given accuracy.
As a result, the energy consumption and overall energy efficiency of inverter air conditioners are significantly improved. Manufacturers give reasonable figures that indicate 30-40% energy savings, all other things being equal.In Full DC-Invertor systems with optimal fan speed control, this gain is even greater.
In countries where the requirements for energy efficiency of consumers are set at the legislative level, "On / Off" air conditioners are practically not used. Thus, in Japan and the EU countries, 100% of new household climate devices are equipped with inverter control systems, in Australia this figure has reached 95%, in China - 80%. Most manufacturers offering high-quality air conditioners on the Russian market (for example, Daikin and Mitsubishi Electric) have stopped supplying non-inverter equipment.
Noise level
The operation of the compressor at minimum power without starting overloads can significantly reduce the noise level during the operation of the air conditioner. Many users ignore this indicator because basic noise during the operation of the split system produces an outdoor unit. However, the current sanitary standards apply to it.
For non-inverter air conditioners, it lies in the range of 40-55 dBA, which, although it meets the requirements, can cause discomfort to both owners and their neighbors. In inverter systems, this figure is reduced to 30-40 dBA.
In Full DC-Invertor systems with smooth control of the fan speed of the indoor unit, it is possible to reduce the noise from its operation to the level of 15-25 dBA (compared to the usual indicators within 25-35 dBA).
Climate indicators
Inverter control of the air conditioner gives a gain in climatic indicators:
- Due to the constant operation of the compressor, the accuracy of maintaining the temperature in the rooms is 0.5-1aboutC (even for ordinary models). This is significantly better than the 2-4 degree accuracy for On/Off mode.
- At the start of the inverter air conditioner, a mode with a power (capacity) exceeding the nominal one is possible. This allows you to reduce the time it takes to set the temperature in the rooms (for some models with this Turbo mode, the gain can be up to 4 times).
- Maintaining a constant air flow temperature significantly reduces the risk of colds. At the same time, devices with regulation of the fan speed of the indoor unit allow you to almost completely get rid of drafts.
- Thanks to the ability to control the compressor performance in a wide range and its constant operation, the system is ensured up to an outdoor air temperature of -10-15aboutC (with special "winter" kits - up to -25aboutFROM).
Reliability
Due to the absence of the most dangerous transients for electrical equipment, the life of the compressor and fan motors in an inverter system can significantly exceed that of conventional air conditioners.
At the same time, the presence of a complex electronic unit and an increase in the number of circuit components lead to some decrease in reliability.
According to the general indicator, inverter systems are superior to non-inverter ones, on average, by 25-40%. However, this is true for high-quality equipment from well-known manufacturers.
Functionality
The inverter air conditioner control system is built, as a rule, on the basis of a microcontroller.
The computing power of modern chips allows not only to control the inverter keys, but also to implement many additional functions:
- Control not only indoor temperature, but also other microclimate parameters, such as humidity, dustiness.
 Accurate measurement of outdoor air parameters and making appropriate corrections to operating modes.
Accurate measurement of outdoor air parameters and making appropriate corrections to operating modes.- Determination of the presence of people in the room.
- "Hot" start with saving the settings after a power failure.
- Indoor air flow control - intensity (by controlling the speed of the fans) and direction (by swinging the blinds in the vertical and horizontal planes).
- System self-diagnosis.
- Control over BlueTooth and/or Wi-Fi channels and other IoT ("Internet of things") and "smart home" functions.
Often asked
Indeed, the repair of an inverter air conditioner is much more expensive than usual, but only in the event of an inverter or control system failure. Other repair options for non-inverter and inverter systems cost the owner almost the same. However, it should be noted that manufacturers give a long-term warranty for equipment (as a rule, at least 3-5, and for premium class - up to 10 years or more). During this time, the purchase of an inverter system pays off already due to energy savings.
Only by saving on electricity, the choice in favor of an inverter system pays off within 3-4 years.
Today, manufacturers of climate technology offer inverter split and multi-split air conditioners, industrial equipment. At the same time, with increasing power, the gain in energy efficiency becomes even more significant.
Due to the use of modern power field-effect or IGBT transistors as inverter keys, the electrical losses on the keys turn out to be scanty (you can judge them by the radiator installed in the electronic unit) against the background of 30-40% energy savings for ordinary models.
Thus, inverter air conditioners are superior to the classic "On / Off" systems in almost all respects. The higher cost of technological devices is more than offset by gains in reliability, energy efficiency and functionality.
Video review comparing inverter and non-inverter air conditioners