Autonomous heating systems are becoming more and more widespread in private houses and even city apartments. The boiler of such a system is controlled by a built-in electronic unit, for the operation of which a stable mains voltage is required. Apartment owners solve this problem by using various types of stabilizers.
Content
- Does the boiler need a stabilizer
- Types of voltage stabilizers for the boiler
- Ferro-resonance stabilizers
- Electromechanical stabilizers
- relay circuits
- Semiconductor (thyristor and triac) circuits
- Two-link (inverter) stabilizers
- The choice of stabilizer according to the parameters of the boiler
- Often asked
- Video tips for choosing a voltage stabilizer for a gas boiler
Does the boiler need a stabilizer
On the forums, in topics where a voltage stabilizer for a gas boiler is discussed, there are directly opposite opinions:
- The stabilizer is not needed, the boiler works fine without it during the entire period of operation.
- The boiler must be connected through a stabilizer, otherwise the probability of its failure is very high.
Both views are supported by facts.
The operating instructions for absolutely all boilers do not indicate special requirements to the supply voltage. They say that the equipment is connected to a household network of 230 (240, depending on the manufacturing country) V, 50 Hz.Additional conditions, such as permissible deviations in voltage and frequency, the content of higher harmonics (non-sinusoidal voltage) are not specified.
In general, this means that the built-in power supply of the electronic unit provides the necessary supply voltage for the circuit at a mains voltage that complies with the standard. At the same time, the normal operation of other electrical equipment included in the boiler installation is also guaranteed, in particular, a pump that creates excess pressure for forced circulation of the coolant.
The European standard establishes a nominal value of the mains voltage of 230 V with a tolerance of +/- 5% for a long time and +/- 10% for a short time. Those. the system will work without failures and failure of components in the range of mains voltages 207-253V.
At the moment, the Russian mains voltage standard is consistent with the European one, the nominal value is 230V, and the permissible deviations are not more than 10% in any direction.
At the same time, manufacturers do not consider as a warranty case the failure of boiler equipment in case of mains voltage deviations that are more than those established by the standard. Accordingly, if drawdowns or surges in the network exceed the permitted limits (voltage drops below 207V or rises above 253V), stabilization becomes necessary.

Many manufacturers of heating equipment may refuse a warranty without a voltage stabilizer in the heating system.
Thus, the user must make a decision to purchase a stabilizer based on his own data on the stability of the network. Of course, in case of deviation from the standard, it is possible to make claims to the provider that provides electricity, including in court, but this process is lengthy and will not help protect the boiler from failure.
Types of voltage stabilizers for the boiler
If measurements of the mains voltage have shown that it may go beyond the permissible limits and the purchase of a stabilizer is recognized as necessary, you should first of all decide on the type of device. At the moment, several variants of schemes are being produced, each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Ferro-resonance stabilizers
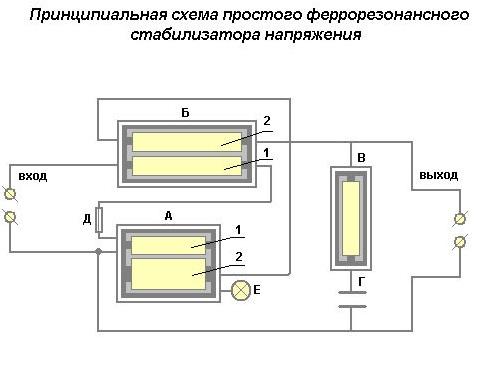
Ferro-resonant devices are well known in Russia since the Soviet times. It was according to this scheme that the first stabilizers produced by the domestic industry were built.
The scheme of such a stabilizer will include 2 windings located on a common core - primary and secondary. Moreover, the section of the magnetic circuit with the primary winding is not saturated, and with the secondary winding it is in saturation mode due to the smaller cross section.
As a result, with increasing voltage changes on the primary winding, the magnetic flux through the secondary winding remains practically unchanged, which ensures the stabilization of the output voltage. The excess current of the primary winding is closed through a magnetic shunt.
Thus, the stabilizer circuit:
- It is as simple as possible, does not have complex electronic components, which ensures high reliability and durability.
- Provides high accuracy of output voltage stabilization and preservation of the sinusoidal form in a wide range of deviations (although the distortion of the output voltage form is not excluded).
- Easily tolerates most external influences, including fairly high humidity and temperature, their differences.
- It has no delays in regulation in case of supply voltage deviations.
The advantages of the scheme are also confirmed by the fact that most of the devices produced in the 50-60s of the last century retain their performance and characteristics today.
However, such stabilizers also have some disadvantages, due to which they are now rarely used:
 Significant weight and dimensions.
Significant weight and dimensions.- Low efficiency and, as a result, the release of a large amount of heat on the circuit elements.
- Noisy operation, characteristic of all devices with powerful winding units, designed for mains voltage.
- Unstable operation in the modes of current overload and idling.
- A fairly narrow range of input voltage deviations, in which stabilization is possible.
All this led to the widespread replacement of ferro-resonant ones with more modern analogues.
Electromechanical stabilizers
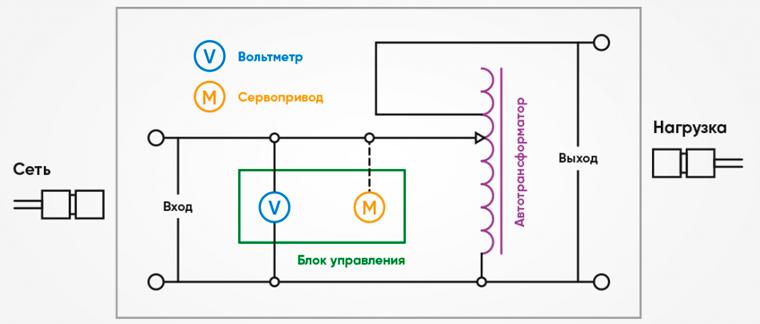
The main component of electromechanical stabilizer circuits is an autotransformer - a device that allows you to change the transformation ratio. This is achieved by moving the current-collecting element along the transformer winding - roller, slider or brush type.
The movement of the contact is carried out by a servo drive, which receives control from an electronic circuit that measures the input voltage and compares it with the set value at the output.
The advantages of such a scheme include:
- Wide range of input voltage deviations.
- High accuracy of output voltage maintenance.
- A cost that is lower than any stabilization device on the market.
The main disadvantage of electromechanical stabilizers is the appearance of an electric arc (spark) during operation. It is caused by breaks in the current flow circuit when moving the movable contact along the turns of the transformer winding. Since the winding has a solid inductance, the interruption of the current causes an arc discharge. Accordingly, it is forbidden to use such equipment in the same room with gas appliances!
However, such a solution can hardly be called rational, especially since the scheme has other disadvantages:
 The already mentioned breaks in the output voltage when the contact moves.
The already mentioned breaks in the output voltage when the contact moves.- Inertia associated with the response time of the servo, which does not allow you to quickly respond to changes in the input voltage.
- Significant weight and dimensions of the autotransformer.
- Insufficient reliability due to the presence of a moving node.
- The need for frequent maintenance of the moving contact.
In a word, when choosing a stabilizer for a boiler, it is recommended to exclude electromechanical devices from consideration.
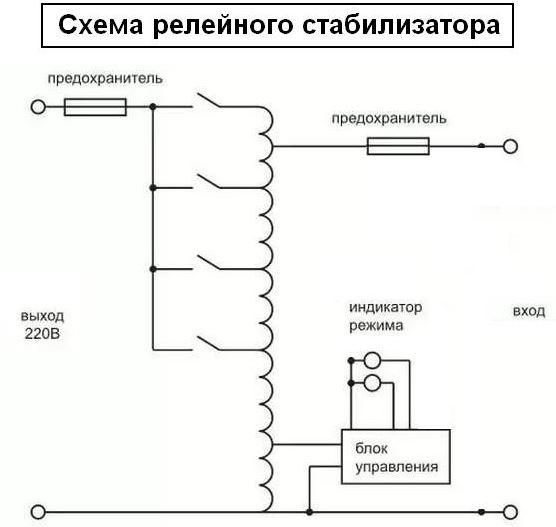
relay circuits
Relay circuits operate with an autotransformer or a transformer with multiple taps in the primary and/or secondary. In this case, the relays act as switches that connect the necessary transformer taps in such a way as to provide a voltage at the output of the device that is as close as possible to the specified voltage.
In fact, this principle of operation resembles electromechanical devices in which voltage stabilization is also carried out by changing the transformation ratio, but not by a moving contact, but by switching a key (relay contact group).
This made it possible to get rid of the main drawback of electromechanical stabilizers - sparking.
In addition, such devices are characterized by other advantages:
 The speed of response to changes in the input voltage, depending on the response time of the relay (it is in the range of 10-20 ms, which is comparable to the time of 0.5-1 period of the mains voltage).
The speed of response to changes in the input voltage, depending on the response time of the relay (it is in the range of 10-20 ms, which is comparable to the time of 0.5-1 period of the mains voltage).- Simple and reliable control scheme.
- Significant MTBF depending on the relays used.
- Maintainability and low cost of replacement components.
- Low sensitivity to current overloads.
The main disadvantages of the circuit are step voltage regulation, which reduces the accuracy of stabilization, the complexity of the winding assembly.
Semiconductor (thyristor and triac) circuits
Devices with semiconductor switches - thyristors and triacs can be built according to two principles:
- Similar to the relay circuit. The difference is only in the use of semiconductor devices, not relay contacts, as a key.
- With the use of a transformer at the input and regulation of the output voltage by changing the opening angle of the thyristors (triacs).
The first circuit is similar in characteristics to the relay one, but has a higher speed. At the same time, a more complex circuit is required to control semiconductor switches, and they themselves have a higher cost, lower overload capacity and MTBF.
In a circuit with an AC voltage regulator, the transformation ratio remains unchanged. The effective value of the voltage is stabilized by controlling the moment of unlocking the keys. This approach makes it possible to simplify and reduce the cost of the winding assembly and the design as a whole.
However, this method of regulation has its own drawbacks, the main of which is the non-sinusoidal output voltage and the high level of interference induced into the network.
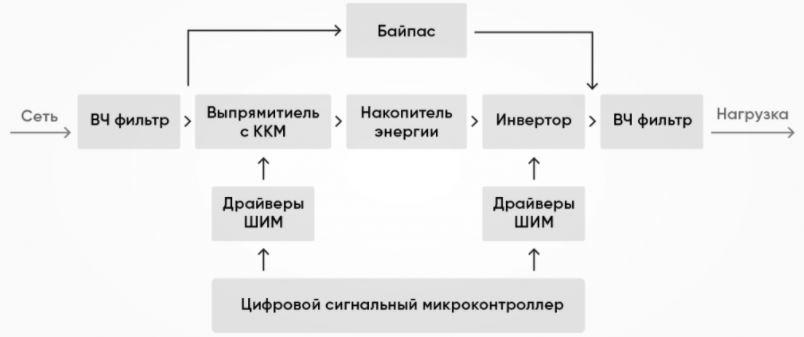
Two-link (inverter) stabilizers
Such circuits are built according to the structure - an uncontrolled rectifier with a filter - an inverter, as a rule, with an output transformer to ensure stabilization during drawdowns.
The circuit has maximum speed, provides high security in all modes, guarantees stabilization accuracy over a wide range of input voltage deviations.
Its main disadvantages:
- The complexity of the control system;
- High price.
In addition, depending on the chosen method of controlling the inverter keys, the output voltage may differ greatly from the sinusoidal one, which adversely affects the operation of the pump.
In general, it is the inverter circuit that can be considered the best option for a boiler in the case when its purchase fits into the owner's budget.
The choice of stabilizer according to the parameters of the boiler
After choosing a stabilizer circuit, it is necessary to decide on a specific model based on the electrical parameters of the boiler.
The only condition for selection is power consumption. It can be found in the technical specifications of the boiler. The buyer is interested in the electrical power, and not in the thermal output of the boiler.
The stabilizer must provide the specified power with a margin of at least 25-30%. The margin is taken from the calculation of the starting currents of the pump, which can exceed the nominal value by several times. However, this process is short-term and the indicated 25-30% is quite enough.
Often asked
Power is the only characteristic parameter. Otherwise, you should pay attention to the protection system and ergonomics of the device.
Since the power of the boiler is small (as a rule, it does not exceed 500 W), the losses on the current-carrying conductors are scanty, therefore, the stabilizer can be located at almost any distance from the boiler within the apartment or house.
Many manufacturers stipulate this as a prerequisite.
From the point of view of providing a stable supply voltage, these options are equivalent. However, the UPS will allow you to properly turn off the boiler in the event of a power failure, in contrast to the stabilizer, which is not designed for such a mode. At the same time, most uninterruptible devices form a rectangular voltage at the output, which is far from the best option for a pump.
Lateral - another name for electromechanical stabilizers, its use in rooms with gas appliances is prohibited.
A stabilizer for a gas boiler will prevent equipment failure in case of significant problems with the supply network. To ensure maximum protection, you should choose the optimal circuit implementation and parameters.
Video tips for choosing a voltage stabilizer for a gas boiler