The hood for a gas boiler in a private house performs two main functions:
- It is necessary for the effective functioning of the equipment;
- The combustion process that takes place in it is impossible without a regular supply of oxygen.

Hood for a gas boiler in a private house
Secondly, ventilation ensures the safety of people living in the house. The circulation of air flows prevents the accumulation of moisture, which, in turn, does not allow the appearance of mold and fungi that are dangerous to health. In case of unforeseen situations, ventilation protects against carbon monoxide intoxication, fires and explosions. In this article, we will consider what components an exhaust system for gas equipment consists of and how to install it yourself in your home.
Content
- Requirements for the room where the gas boiler is located
- How to choose the material for the hood?
- Video - device and installation of a chimney and hood for a gas boiler
- Natural and forced ventilation of the boiler room
- Calculation of the ventilation system
- Installation of natural ventilation
- artificial ventilation
Requirements for the room where the gas boiler is located
Low power boilers (up to 30 kW) can be placed in the kitchen if it meets a number of requirements:
- kitchen area is at least 15 m2;
- the ceiling is located at a height of 2.2 m and above;
- sufficient glazing (total area of windows) - at least 3 cm2 us3 kitchens;
- windows are equipped with transoms and vents;
- there is a distance of 10 cm between the gas device and the wall;
- the walls are finished with fire-resistant material;
- air flow is ensured through cracks, for example, at the bottom of the door.
In order for powerful appliances (from 30 kW) to serve for a long time and be safe at the same time, experts strongly recommend equipping a separate room - a boiler room. Of course, not every room in the house is suitable for such purposes. Its volume must be at least 13.5 m3 for devices with a power of 30-60 kW and at least 15 m3 for 60 kW.
How to choose the material for the hood?
For these purposes, brick, galvanized and stainless steel and ceramics can be used. Let's take a closer look at each of them, and also explore what other options the market and engineering offers.
Masonry hood
Although brick is used by builders in arranging ventilation, its properties do not allow saving on other materials. First, brickwork is short-lived. The most comfortable for her are the conditions of constant contact with hot gases. Otherwise, condensation will form, which leads to its rapid destruction. Secondly, a brick chimney is laborious to install, has a complex design and unreasonably high cost. Therefore, if you are faced with the task of arranging a chimney for a gas boiler, it is better to pay attention to other options. In this situation, a mine is made of bricks. The same option can be chosen if for some reason it is not possible to heat the house with gas now, but in the future it is planned to use it.
If brickwork is chosen as the material for the shaft, then the chimney itself is assembled from single-circuit galvanized pipes. The thickness of their walls is selected taking into account the temperature of the outlet gases.
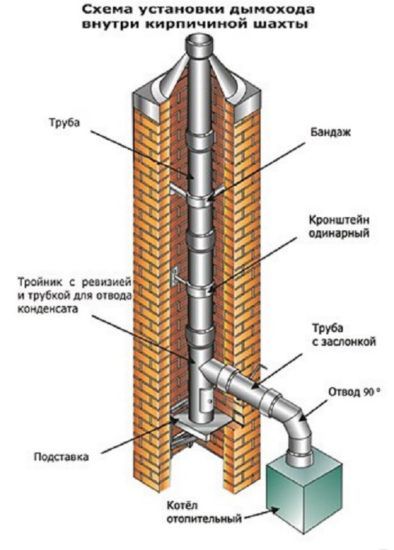
Components of a chimney inside a brick shaft
Steel hood
In this situation, steel pipes are very convenient. They are easy to install when compared, for example, with brickwork. The wall thickness is chosen depending on the heating. Gas boilers produce a fairly hot exhaust gas, about 400-450˚С, so the walls should be 0.5-0.6 mm thick. However, there are pitfalls here as well. Of course, steel is resistant to the negative effects of condensate. But on average, its wear resistance is much lower than, for example, the wear resistance of ceramic products. In addition, thin-walled pipes burn out quickly if used with solid fuel devices, so this option is not optimal if different types of heating elements are used at different times. Steel choose:
- during reconstruction;
- if there is no space for a ceramic hood.
Since steel ventilation ducts often spoil the exterior of a private house, they are covered with brickwork or other finishing materials.
Steel pipes are put on the market in two variations - single-circuit and double-circuit. The second option is called "sandwich" in jargon. It consists of two pipes nested one inside the other, the gap between which is filled with refractory basalt wool. The thickness of the inner pipe is determined by the temperature of the outlet gases (recall that this value is 0.5-0.6 mm for the devices considered in the article).
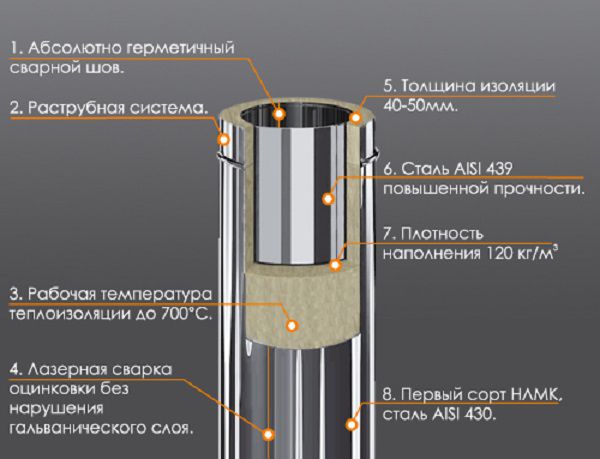
The device of a steel double-circuit chimney
"Sandwiches" are considered more economical among all steel hood options. Such a conclusion suggests itself, if we take into account good thermal insulation, which increases the efficiency of the heater.
Double-circuit steel chimneys are made of stainless and galvanized steel. Both metals are combined in "sandwiches", since it is not economically feasible to use only stainless steel. The difference between galvanized and stainless steel is the higher resistance of the latter to condensation, which negatively affects its price. Otherwise, the properties of these two materials are not inferior to each other.
It is critical that the inner part of the double-circuit structure is made of stainless steel, the material of the outer part does not play a special role. This is due to the properties of zinc. Its heating higher than 419.5 ° C is dangerous. In this situation, the metal is oxidized, a further chemical reaction leads to the release of toxic fumes. Everything becomes even worse with high humidity, which cannot be avoided when commissioning a gas boiler. Therefore, when buying a sandwich structure, pay attention to this.
In principle, a double-circuit chimney can be made independently, without having any special skills. To do this, wrap the stainless steel pipe in a refractory heat-insulating material. When choosing the latter, you can pay attention to basalt fiber, expanded clay or polyurethane. Then place everything together in a galvanized pipe of a larger diameter.
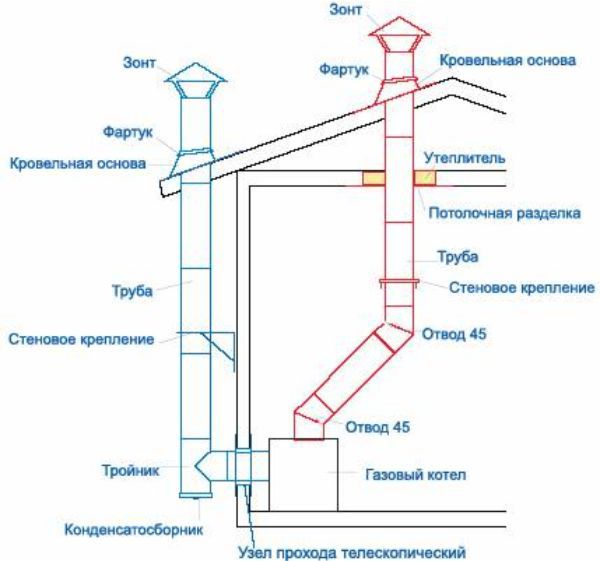
Scheme of mounting a steel hood
Features of installing a steel ventilation pole:
- Segments are assembled using the pipe-to-pipe method in order, starting from the bottom;
- For the convenience of subsequent cleaning of the column, provide a sufficient number of revision wells;
- For stability, wall brackets are attached in approximately 150 cm increments;
- When designing, pay attention to the horizontal segments - they cannot be more than 1 meter long, unless forced draft is provided.

Stainless steel ventilation duct
Ceramic hood
This type of hood is the most versatile, so it is ideal if you plan to switch from or to gas fuel. They are easy to clean, resistant to pollution, due to high gas density and aggressive chemical compounds, so you don’t have to worry about the ingress of toxic substances into living rooms. And, of course, ceramics are durable.
But there are also disadvantages. Ceramic pipes have high moisture absorption. If you opted for them, you will have to provide good external ventilation and provide the structure with steam traps, otherwise the effort and money invested will not justify itself.
Ceramics alone are not used in chimneys. To maximize its positive properties, it is combined with mineral wool and stone. Simply put, the ceramic pipe is wrapped in an insulating material and then placed in an expanded clay concrete shell.
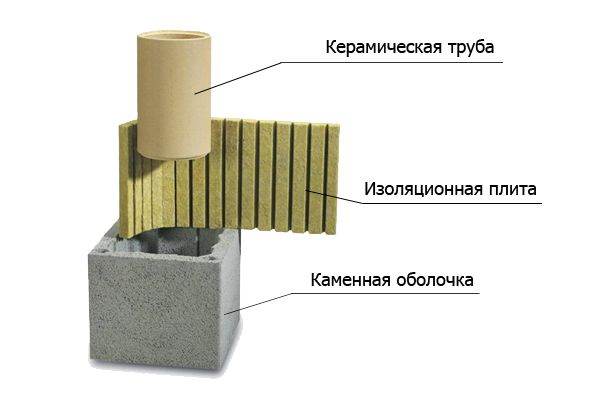
The structure of the ceramic chimney
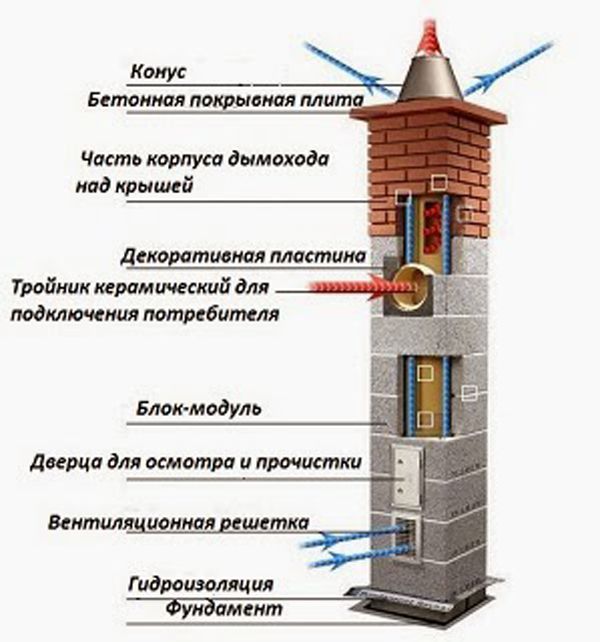
Construction of ceramic hood
Structure of coaxial ventilation
When designing ventilation for gas boilers, pay attention to the compact pipe-in-pipe design, or, in other words, a coaxial chimney.
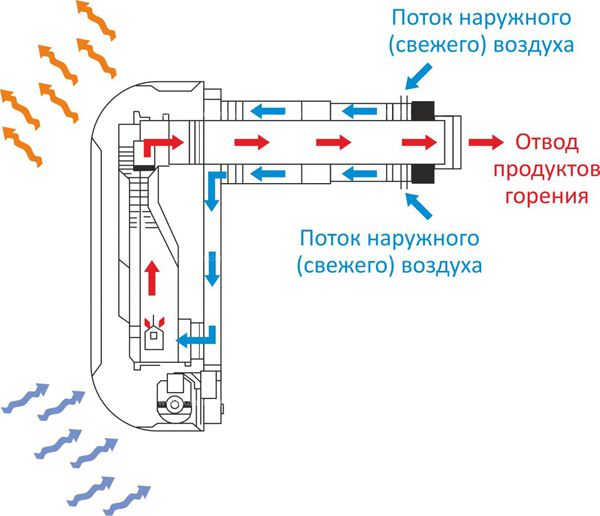
The principle of operation of the coaxial ventilation system

Components of a coaxial chimney
Coaxial systems, due to their characteristics, are suitable for heat generators with a closed combustion chamber (which is a gas boiler). The oxygen necessary for combustion enters through the outer pipe, and the exhaust gases are removed through the inner one. This design has its advantages:
- safety (exhaust gases are cooled by cold air circulating in the outer pipe);
- the incoming air is heated and increases the efficiency of the boiler;
- high efficiency means that the coaxial design is more environmentally friendly;
- can be used with the appliance in the kitchen (located outside the room and does not affect comfort in it).
Features of installing a coaxial chimney
- a horizontal coaxial chimney cannot be used if forced draft is not planned;
- try to get by with no more than two knees;
- if there are several boilers, form a separate chimney for each, combination is undesirable.
Video - device and installation of a chimney and hood for a gas boiler
Natural and forced ventilation of the boiler room
According to the method of updating the airspace, natural and artificial (or forced) ventilation are distinguished.
Natural ventilation operates without the use of fans, its efficiency is due solely to natural draft, and, consequently, weather conditions. Two aspects affect the pull force: the height of the exhaust column and the temperature difference between the room and the street. At the same time, the air temperature in the street must necessarily be lower than that in the room. If this condition is not met, reverse draft occurs and ventilation of the boiler room is not ensured.
Forced ventilation provides for the installation of additional exhaust fans.
Usually these types are combined into one exhaust system of the boiler room. When calculating it, it is important to take into account that the volume of air drawn out into the street should be equal in volume to that injected into the room. To ensure that this condition is met, check valves are installed.
Calculation of the ventilation system
According to building standards, the entire airspace of the boiler room must be replaced with a new one every 20 minutes. To ensure the appropriate air circulation, you will have to arm yourself with a calculator and formulas.
If the ceilings are located at a height of 6 meters, then without special devices the air in the room is updated three times per hour. Six-meter ceilings are a luxury for a private house. The decrease in ceilings is compensated for in calculations in the following proportion - for every meter below, air exchange increases by 25%.
Suppose there is a boiler room with dimensions: length - 3 m, width - 4 m, height - 3.5 m. To solve this problem, you need to perform a number of actions.
Step 1. Find out the volume of airspace. We use the formula v \u003d b * l * h, where b is the width, l is the length, h is the height of the ceiling. In our example, the volume will be 3 m * 4 m * 3.5 m = 42 m3.
Step 2. Let's make a correction for a low ceiling according to the formula: k \u003d (6 - h) * 0.25 + 3, where h is the height of the room. In our boiler room, the correction turned out: (6 m - 3.5 m) * 0.25 + 3 ≈ 3.6.
Step 3. Calculate the air exchange provided by natural ventilation. Formula: V = k * v, where v is the volume of air in the room, k is the correction for lowering the height of the ceiling. We got a volume equal to 151.2 m3 (3.6 * 42 m3 = 151.2 m3).
Step 4It remains to obtain the value of the cross-sectional area of the exhaust pipe: S = V / (w * t), where V is the air exchange calculated above, w is the air flow velocity (in these calculations it is taken as 1 m / s) and t is the time in seconds. We get: 151.2 m3 / (1 m/s * 3600 s) = 0.042 m2 = 4.2 cm2.
The dimensions of the channel also depend on the area of the inner surface of the boiler. This number is indicated by the manufacturer in the technical documentation of the device. If this number is not indicated, calculate it yourself based on the volume of the device. Then compare the area with the section radius according to the inequality:
2πR*L > S, where
R is the inner radius of the chimney section,
L is its length,
S is the area of the inner surface of the boiler.
If for some reason such a calculation is difficult, you can use the table.
| Boiler power, kW | Chimney pipe diameter, mm |
|---|---|
| 24 | 120 |
| 30 | 130 |
| 40 | 170 |
| 60 | 190 |
| 80 | 220 |
The last stage of the calculation is the height of the weather vane relative to the roof ridge. The need for this is due to the creation of additional traction by the wind, which increases the efficiency of the entire exhaust structure. At this stage, the following principles are followed:
- the height of the wind vane above a flat roof, or at a distance of up to 1.5 meters from its ridge, must be at least 0.5 meters;
- at a distance of 1.5 to 3 meters - not lower than the roof ridge;
- at a distance of more than 3 meters - not lower than a conditional line drawn from the roof ridge at an angle of 10˚;
- the weather vane should be 0.5 meters higher than the building, which is attached to the heated room;
- if the roof is made of combustible materials, the chimney must be raised 1-1.5 meters above the roof ridge.
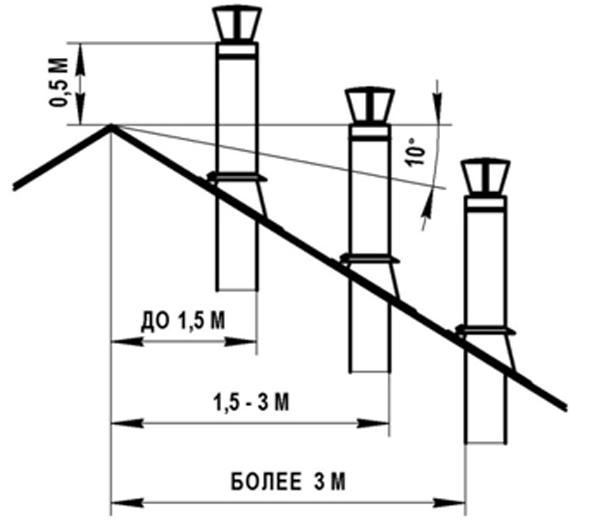
Calculation of the height of the chimney relative to the roof
Installation of natural ventilation
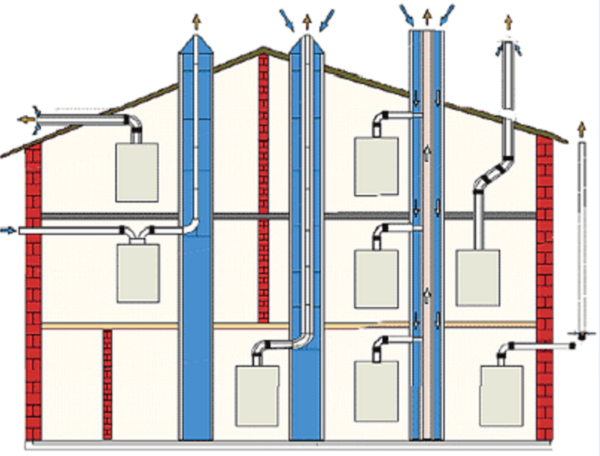
Ventilation system placement options
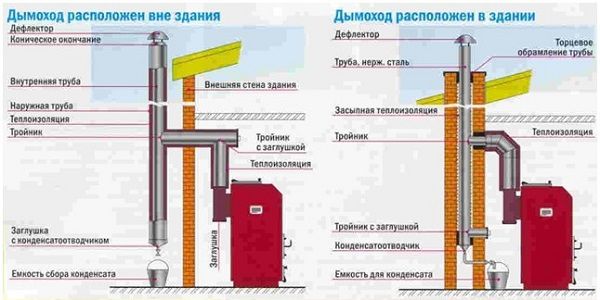
The design of the chimney depending on the location
Natural ventilation in the boiler room is provided by installing supply and exhaust ducts.
To install the supply channel you need:
- Pick up a piece of plastic pipe, a suitable grate and a non-return valve. The diameter of the first is selected taking into account the power of the boiler. If the power is less than 30 kW, 15 cm is enough. Higher power - larger diameter.
- In order for air to pass directly into the furnace, a through hole to the street is punched next to the heater and not above its working area. Then a pipe is placed in the hole, the gaps inside are filled with mortar or mounting foam.
- From the outside, the opening is closed with a fine grate to protect it from dirt and animals. A non-return valve must be installed from the inside to prevent back draft to the street.
The exhaust channel is brought out through the hole above the boiler at the top of the room. Usually it is also equipped with a check valve that prevents air from entering from the street. The chimney can also be equipped with a protective rain cover or weather vane, steam traps and inspection windows for cleaning.
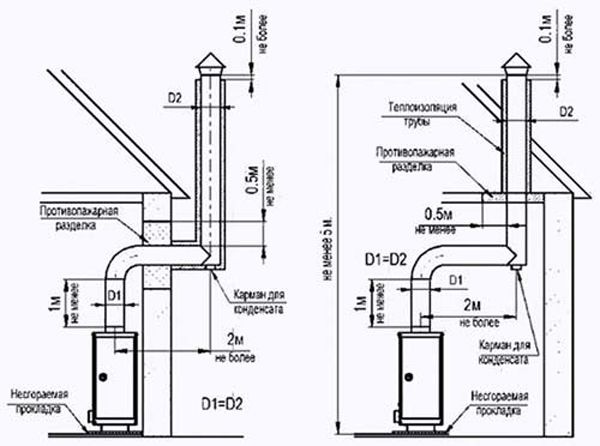
Ventilation system design diagram
artificial ventilation
Additional draft in the exhaust system is created with the help of fans. Their power and number depends on the air load on the channel and the volume of the room.
- power is taken from the calculation: maximum load plus a margin of 25-30%:
max * 1.25, where max is the maximum load;
- the number of devices is selected in proportion to the volume of air required for pumping (increase the volume of the room three times):
(h + b + l) * 3, where h is the height of the ceiling, b is the width, l is the length;
- the length of the chimney, its geometry and the number of bends are taken into account.
The fan is protected by an installation box.This box is made of non-flammable and stainless materials. Usually copper or aluminum alloys are used.
The design of artificial ventilation is similar to the installation of natural. After installing the supply pipe, the duct fan is installed. Next, the builders lay the wiring to power the engine, install sensors, a noise absorber and a filter. Just as with the installation of natural ventilation, gratings are attached to both ends of the pipe. The device for the exhaust pipe is installed in the same way, with the only consideration that the air is drawn out and not blown in.
Artificial ventilation requires constant energy costs. Sometimes they save money during construction by installing a fan only on the exhaust or only on the air supply. However, more efficient circulation is achieved by using both.
The automatic ventilation system allows you to turn off the fans when the boiler is stopped and turn them on when the boiler is started.












