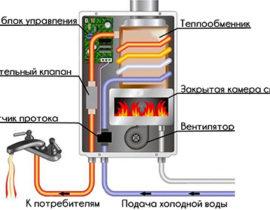
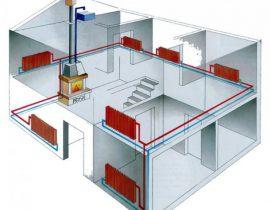
Autonomous heating systems are very popular in suburban construction. Their creation allows the owner of the home to feel independent of utilities, save significantly on heating bills. Moreover, in some cases, connection to the main heat supply system is simply impossible. In general terms, an individual heating system in a private house with a liquid coolant consists of a device that heats water (it can operate on different types of fuel) and a hot coolant circulation system.
The design and construction of a water circulation system plays an important role in creating a high-quality autonomous heating system. It consists of several components, and among them the expansion tank for heating plays an important role, if not the decisive one! For the full functioning of the system, the tank is simply necessary, it makes the system more complete and without it, functioning is impossible in principle! It's like a car that can only drive if all its components and assemblies are set up and functioning properly!
Content
The main functions of the expansion tank for heating or why is it needed at all?
The expansion tank in individual heating systems has an important role in receiving the excess part of the heat carrier water. When heated, water can change its volume, and in heating systems, the temperature of the coolant is not a constant value. Thus, when creating a completely closed hermetic hot water circulation system, there is a significant risk of rupture of the connecting elements as a result of pressure increase. Water is a practically incompressible substance and even the most reliable connection made of brazed plastic, as well as any metal, cannot resist its pressure.
Consider how an expansion tank works in an individual heating system, what types of expansion tanks are, how to choose this equipment correctly, and what subtleties must be taken into account when installing it in a private house.
Principles of operation of the expansion tank
Let's take a simple physical example. Suppose the temperature of the liquid heat carrier-water in our heating system has risen by only 10 degrees. This may be due to the more intensive operation of the heating device, caused by a lower temperature outside. After such a rise in temperature, the volume of water circulating in a closed system will increase by 0.3 percent.
It would seem - not a very large value. However, water (or antifreeze used as a coolant) is incompressible, that is, a strong overpressure gradually builds up in the system. To prevent such pressure from destroying the connecting elements of the heating system, water must be given space to expand.This space will be the expansion tank. With a cold coolant, it is not completely filled, but when heated, the water level in it increases, which keeps the pressure in the water circulation system at a normal level.
Expansion tank device
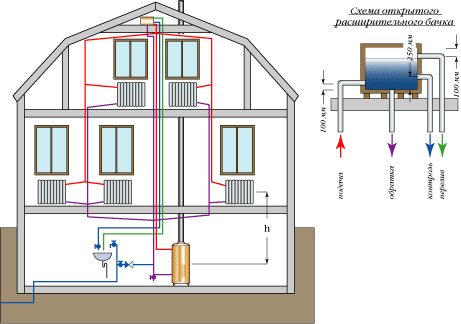
In an individual heating system with a liquid heat carrier installed and ready for operation, the expansion tank looks something like the one shown in the figure (Fig. 2). In some literature, this device is called an "expansomat" - from the English term "expansion" - expansion).
There are the following main types of expansion tanks for heating systems:
- Tank of the closed type.
- Tank of open type.
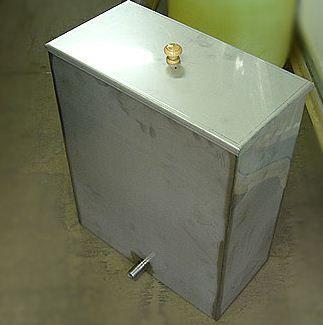
Expansion tank open type
In older heating systems, an open-type expansion tank was often used. Until now, such devices are mounted in systems in which there are no circulation pumps that ensure the circulation of the coolant.
However, the tank of such a system has its drawbacks:
- First of all, in such a system it is necessary to constantly monitor the level of the coolant.
- Water from such a system can evaporate.
- Open-type tanks quickly rust when in contact with water.
- The design of the system with an open-type tank involves its installation exclusively at the upper point, which is not always possible, and is simply laborious.
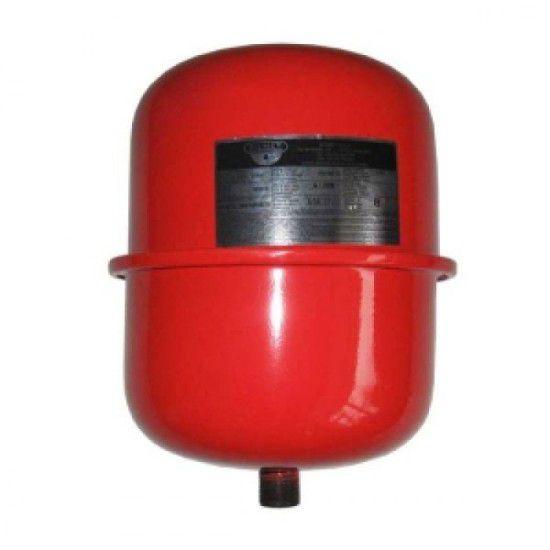
Expansion tank closed type
In systems in which the coolant circulates through the circuits through operating pumps, only expansion tanks of a closed type are installed.
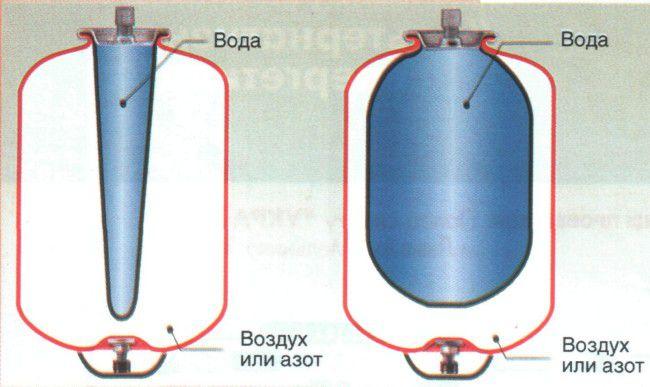
This is a more complex device, in which there is a special membrane located in a hermetically sealed container for the coolant.
Membranes in such tanks are divided into diaphragm and balloon. In any case, the membrane divides the container into two parts. The first contains an inert gas pumped under pressure (to prevent corrosion) or ordinary air, and the second, when the pressure in the heating system rises, excess coolant enters.
As soon as the temperature of the coolant in such a system increases, its excess part rushes into the expansion tank. The membrane changes its configuration (like a balloon) and the volume of air or gas in another part of the expansion tank decreases. Gases, as you know, are quite easily compressed, but also tend to expand.
When the coolant cools, the expanding gases push the membrane and push the excess coolant back into the heating system.
Types of closed expansion tanks
With the same basic device, expansion tanks of a closed type can be divided into several more types:
- A tank with a replaceable membrane, also called a flanged one.
- Tank with non-replaceable membrane.
The cost of tanks of the second type is lower and they are more popular with consumers. However, replaceable diaphragm tanks can withstand large pressure drops in the system, dramatically increasing their efficiency. In addition, they are more maintainable and the membrane can be replaced if damaged.
Flanged expansion tank can be made in two versions: vertical and horizontal. A distinctive feature of expansion tanks of this type is the absence of contact between the coolant and the surface of the tank. Expanding liquid is located inside a kind of membrane cocoon, so there are no reasons for corrosion on the surface of the tank.It is quite easy to change such a membrane: the flange is simply unscrewed and repair work is carried out.
In membrane expansion tanks, the greatest risk of damage to the membrane element occurs at the time of system start-up, when the pressure in it increases abruptly.
When large volumes of coolant are in the system, the normal pressure level is produced by means of a pressure gauge. Such a device is connected to a safety valve, the threshold value for which in a private house is set to 3-4 bar.
How to choose and install an expansion tank
First of all, the selected expansion tank in terms of its geometric dimensions must correspond to the volume of the coolant in the system. Pay special attention to this when choosing. Purchasing an overly small tank can reduce all its effectiveness to zero.
Pay special attention to the characteristics of the membrane device. It must retain its working properties over the entire temperature range planned in the heating system. Also, the membrane must withstand possible pressure surges, for which it must have a certain margin of flexibility.
It is necessary to install an expansion tank in the heating system of a private house according to the prepared project, if you yourself are not able to prepare such a project, be sure to seek help from professionals!
Remember that open tanks for expanding the coolant can only be installed in the upper part of the heating system. Usually they have a threaded connection located at the bottom of the device.
At the same time, a closed-type expansion tank can be installed anywhere in the heating system. It is desirable that the place of its installation is directly after the circulation pump in the direction of the coolant.
Please note that an expansion tank of any type, when filled with water, significantly increases its mass, which imposes additional requirements on the strength of its fastening system. Provide free access to the heating tank, especially to devices with a replaceable membrane.
When installing an expansion tank, it is mandatory to install a pressure gauge and a safety valve in the heating system, which will serve as the “last line of defense” in case of unplanned excessive expansion of the coolant.
If you carefully select and correctly mount everything, you can be sure of a long and uninterrupted operation of the heating circuits.
Training video on the operation of an expansion tank for heating in a private house