The Leningradka heating system appeared in the middle of the 20th century. Its main features are ease of arrangement, efficiency and the ability to heat rooms of a rather large area. Thanks to these qualities, "Leningradka" quickly gained wide popularity, which it has not lost to this day. Let's talk about the system in more detail.
Content
- Device and system features
- Design
- Principle of operation
- Pros and cons of the system
- Installation of "Leningrad": the choice of the type of system, the procedure for work, the nuances
- Type selection
- materials
- Carrying out work
- The nuances of the work
- Questions and answers
- Reviews
- conclusions
- Video review of the Leningradka heating system
Device and system features
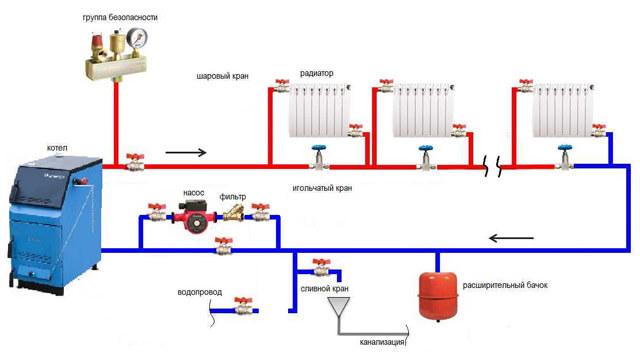
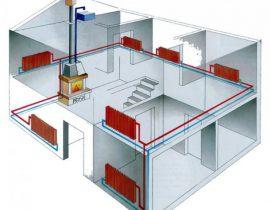
"Leningradka" can be defined as a closed heating system in which heating devices are connected in one circuit. A gas boiler is used as a heat generator. The most common heat carrier is water.
Design
The simplest version of the system consists of the following elements:
- Expansion tank. It is a reservoir with a coolant. It is installed above the heating elements and the boiler in order to ensure the circulation of water through the pipes.
- Boiler. Connects directly to the expansion tank and the upper circuit. Heats up the coolant.
- Upper outline. It supplies hot water from the boiler to the tank and heating elements.
- Bottom outline. It removes the cooled coolant from the heating elements to the boiler for subsequent heating.
The main feature of the "Leningrad" is that the heating elements are not connected to the upper circuit in series, but are installed in parallel to it. This is the main difference from the usual single pipe heating system.
Principle of operation
The principle of operation of the Leningradka, in general, does not differ from that in any one-pipe heating system.
 The system functions as follows:
The system functions as follows:
- the boiler heats the water and supplies it partially to the upper circuit, and partially to the expansion tank (excess coolant enters there;
- the heated coolant is lighter than the cold one, therefore it rises into the battery, displacing the cold one down;
- in the battery, the water gives up its heat, and is itself displaced by the hotter one that has just come from the boiler;
- the cooled coolant enters the lower circuit, which leads to the entrance to the boiler;
- after cold water enters the boiler, the cycle repeats.
Pros and cons of the system
The advantages of "Leningradka" include:
- Simplicity. Despite some complications compared to the traditional one-pipe system, the "Leningrad" is very simple. Its installation is within the power of even those who do not have specific knowledge and skills in the relevant field.
- frugality. 20% - 30% less material is spent on Leningradka. But here we must immediately make a reservation - the advantage is relevant only in comparison with two-pipe system. If you take a single-pipe, then it will turn out to be even somewhat more economical (due to the fact that the batteries are connected in series and no taps are made to them).
- Possibility of fine tuning. If you install a needle regulator on each bypass, it becomes possible to regulate the temperature of a single battery.
- Ease of maintenance. If we are talking about a traditional one-pipe system, it will have to be completely freed from water to replace the battery. In the case of the "Leningrad" this is not necessary - it is enough to block the bypass. Water will continue to circulate through the lower circuit. True, in order to have such an opportunity, it is necessary to equip bypasses with cranes.
However, the system also has disadvantages. Here are the main ones:
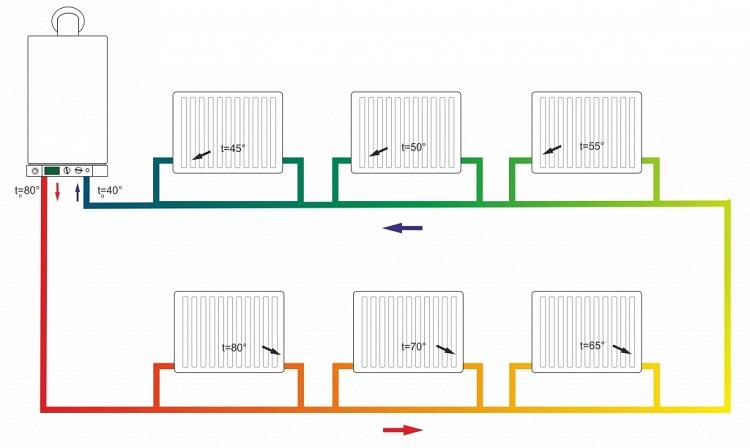
- Uneven heating of radiators. Even a needle valve in the bypass does not solve the problem. True, it does not occur with all types of connections. But more on that later.
- Inability to connect additional heating equipment. For example, a warm floor. But this is not a drawback exclusively of the "Leningrad" - a minus is typical for any one-pipe heating.
- The need to use large diameter pipes. The minimum should be at least 2.5 cm. If you take less, it will be difficult to find suitable bypasses for radiators. Because of this, there is often a drop in pressure in the system. As a result, water cannot circulate normally. The problem is solved by installing pipes of smaller diameter, which create the necessary pressure.
Installation of "Leningrad": the choice of the type of system, the procedure for work, the nuances
Further - detailed instructions for the installation of "Leningrad".
Type selection
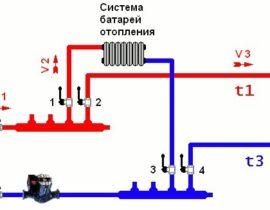
First you need to decide on the type of "Leningrad". The differences come down solely to the type of battery connection.
Depending on this criterion, four types of system are distinguished:
- with bottom connection;
- with vertical connection;
- with top connection;
- with a diagonal connection.
The bottom normally warms up only half of the battery. In addition, when using them, difficulties with the circulation of the coolant are possible. They are solved by connecting an electric pump that will pump water through the system. But this reduces the advantages of "Leningradka" to nothing. After all, the pump increases the cost of electricity. Yes, you will have to buy the device.
The best option is a vertical connection. It ensures even distribution of water in the system, which gives the best heating of the radiator. Diagonal connection has similar characteristics.
The top connection can also work without a pump. But during installation, it is necessary to correctly determine the geometry of the pipes. If you assemble the accelerating section incorrectly, there will also be problems with water circulation. Proper installation requires a little more consumables. This also eliminates the advantages of the system over traditional options.
materials
The choice of pipes for creating a system depends on:
- the number of radiators;
- warming up the system.
The diameter of the pipe must be such as to provide the required number of batteries with the coolant. The more of them, the wider the gap should be. For 4 radiators you need at least 2.5 cm. For 5 - 6 - approximately 2.7 - 2.8 cm.
Depending on the heating, the material of the pipe is selected. If the water in the system reaches temperatures above 90about C, it is better to use steel. The fact is that polypropylene melts already at 95about FROM.
Radiators are selected based on the efficiency of their work. They should have maximum heat dissipation. This is especially important because already slightly cooled water gets into the last batteries of the circuit.So for full heat transfer, they must have a high efficiency.
Carrying out work
When you have decided on the connection diagram and selected materials, you can begin work on assembling the system.
They consist of the following steps (using the example of a vertical connection of radiators):
- Training. At this stage, pipe holders are installed. If it is planned to hide them in the walls, strobes are prepared.
- Boiler installation. Install a heating boiler.
- Laying the main line. Two pipe loops are laid from the boiler: upper and lower.
- Branches are made in the upper circuit. If we are talking about polypropylene pipes, then the bends are created using tees. If the pipes are metal, then a hole is made in them, where a bypass of a smaller diameter is welded.
- If necessary, taps are mounted in the bypasses to block the access of the coolant or adjust the temperature of the battery.
- Radiators are connected to bypasses.
- An expansion tank is connected to the outlet of the upper circuit of the system.
All work completed. You can fill the system with water.
The nuances of the work
In the course of work, you need to remember the following features:
- If metal pipes are used, internal sagging must be avoided when welding. They reduce the internal clearance and prevent the normal movement of the coolant. In the presence of influxes, the system will not work normally.
- After filling the system, do not immediately conduct a test run. Before him, you need to wait 3 - 4 hours and check all sections of the pipe, its connection with radiators, boiler, tank. This will allow timely detection and elimination of leaks.
- Before a test run, be sure to remove air from the system using Mayevsky craneslocated in the radiators. Otherwise, it will warm up only partially (in the area up to the air bubble).
If there is no pump in the system, the upper circuit should be located with a slight slope (approximately 5 - 10about). This will facilitate the flow of the coolant and prevent the problem of water stagnation in a certain section of the pipe.
Questions and answers
Yes, since the first radiator often gets too hot. On the latter, a crane is not needed.
When connected vertically, no. But if the angle of inclination of the upper circuit is incorrectly determined, the water will not circulate normally through the system.
Yes. The difference can reach 45% - 50%. That is why it is so important to ensure the correct circulation of the coolant.
Only if it's open. Closed can work without insulation in an unheated attic.
Reviews
- Konstantin, Tula region
“I have a small country house. I often go there in winter, so I installed gas and decided to make heating. The choice was stopped at "Leningrad". A two-pipe system is too expensive for me, and a single-pipe system is inconvenient - it’s difficult to maintain radiators, you can’t turn off a single battery. I did not take the pump, I connected the radiators diagonally. I've been using it for almost a whole winter, so far there were no complaints - I'm happy with everything. I can say one thing: "Leningrad" fully met my expectations.
- Ivan, Novgorod region
“They brought gas to the parents in the village house. The question arose about the arrangement of the heating system. We decided to make "Leningrad". The area of the house is small - there are only 6 radiators. There is no point in a two-pipe system. As long as everyone is happy. Heats well enough (I connected the batteries vertically). Works great without a pump, although many say that it is necessary. Separately, I want to say about the savings - the expenses turned out to be very small.
conclusions
"Leningradka" - a kind of one-pipe heating system. Unlike the traditional scheme, it provides for the parallel connection of radiators through bypasses. The system is simple, cheap and easy to maintain. Ideal for heating small areas (primarily cottages and country houses).
Video review of the Leningradka heating system