Underfloor heating is an economical and efficient way to heat rooms. However, adjustment and adjustment of the coolant supply mode require the use of specialized units designed for use in certain systems.
One of the most important devices is the collector, which provides distribution and organization of the coolant supply, as well as the reception of the reverse flow. The principle of operation and the device of the collector are very simple, but the tasks that it performs should be attributed to the most important and responsible functions. Let's take a closer look at the features and specifics of the collector's work.
Content
General arrangement of a water-heated floor

General view of the underfloor heating device
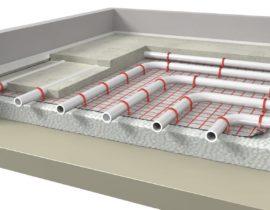
Underfloor heating is one of the ways to heat rooms, providing significant savings and a high level of comfort. From a technical point of view, this is a pipeline with a circulating coolant distributed over the entire floor area. In fact, this is one big radiator. However, there are serious differences.
First of all, they relate to the temperature regime. If a coolant with a standard degree of heating is directed to the warm floor - about 80 ° -85 °, then sauna conditions will arise in the room. Therefore, the coolant temperature never exceeds 45°-50°.This allows you to seriously save on fuel or electricity consumed for the preparation of the coolant.
The relatively low temperature of the working fluid puts forward its own requirements for laying pattern warm floor. It is impossible to use one long pipeline - in the initial sections, the coolant will have a given temperature, but then it will cool down and will not fulfill its tasks. in addition, reheating the cooled coolant will require a large fuel consumption. Therefore, the pipeline is divided into uniform segments (they are called loops). Water circulating through a relatively short pipeline cools down much less. Its temperature is easier to raise to the standard, which makes the heating system the most economical.
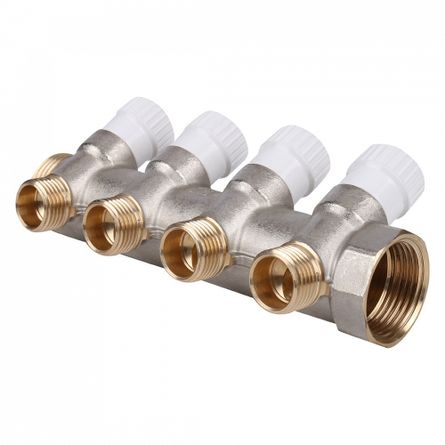
What is a collector

Collector for underfloor heating
The collector (specialists sometimes call it a comb) is the simplest distribution unit in the underfloor heating system. It has the form of a pipe segment, to one of the ends of which a direct or reverse coolant supply line is connected. The second end is usually plugged, or an air valve is installed on it. Along the entire length of the pipe there are holes designed for connecting floor heating loops. The holes are through, on the one hand you can attach a pipe, and on the other - install a control.
The task of the collector is to distribute the flow of the coolant through the loops of the warm floor. Each loop connects to one of the outputs. The coolant passes along its entire length and enters the second collector connected to the return line.
For normal operation of the system, two collectors are needed, therefore, collector groups are usually used to assemble a warm floor - sets of two devices connected by a bypass, temperature and pressure measuring instruments, and a built-in circulation pump.
The use of such nodes facilitates the installation of underfloor heating controls, although in some cases it is necessary to use separate elements and assemble non-standard designs from them.
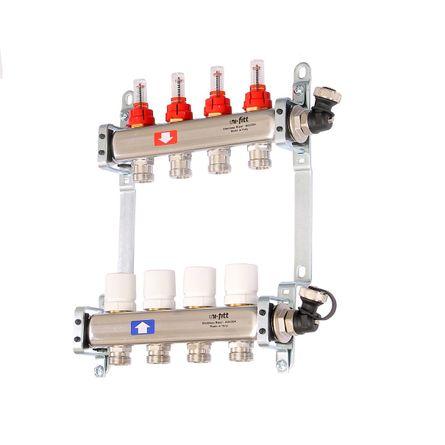
Advantages and disadvantages of underfloor heating collectors

Visibility of connecting a warm floor
The advantages and disadvantages of collectors include:
- effective distribution of the coolant flow over all loops of the warm floor;
- the ability to block the flow on separate loops, or change the feed mode;
- ease and convenience of adjusting the heating mode;
- visibility of the connection, the ability to visually determine the number of loops;
- ease of repair or replacement of the device;
- the ability to change the number of loops by connecting new circuits or installing additional nodes.
- mode adjustment requires some experience - a water-heated floor has a large inertia and does not immediately respond to changes in the mode of supply of the coolant;
- the number of loops that can be connected to the collector is structurally limited;
- in the event of failure of valves, regulators or connecting elements, leakage is possible;
- the cost of the collector is quite high compared to the price of conventional components for heating systems.
The disadvantages of the collector are, rather, the features of its design. As a rule, users refer to them from these positions. If the connection and operation are carried out without violations, there will be no problems with the collector.In any case, it is impossible to do without this node, therefore, it is more correct to treat its properties with understanding.
Composition of the collector group
By itself, the collector is only a separate part of the collector node (or group). It consists of the following elements:

supply manifold
A common pipeline with a hot coolant and underfloor heating loops are connected to it, into which a hot stream enters;

return manifold
This element performs the opposite function - it receives a cooled coolant that has passed along the entire length of each loop. After that, the liquid enters for re-treatment;
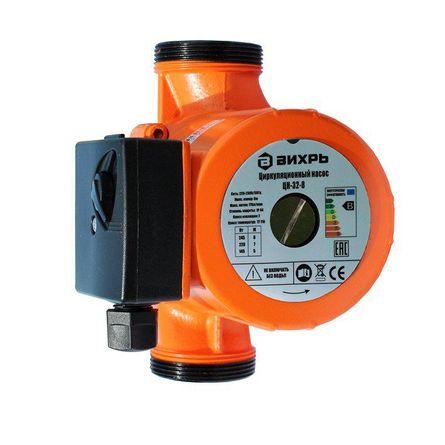

circulation pump
It provides operating pressure in the underfloor heating system. Sometimes you can do without it if the number and length of the loops are small, and the underfloor heating is powered from your own boiler. In such cases, the pressure from the pump built into the boiler may be sufficient;
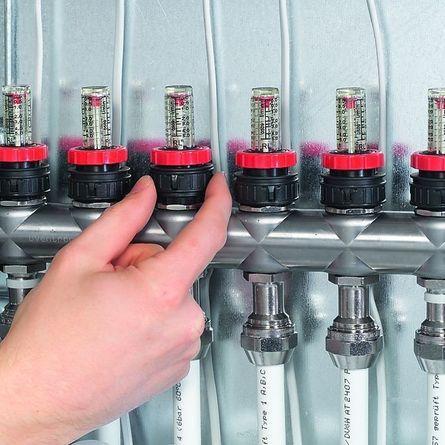

devices for adjusting the heating mode
There are flow meters on the direct manifold above each outlet, and valves on the return. Sometimes valves with a servo drive are installed at the inlet, capable of adjusting automatically;
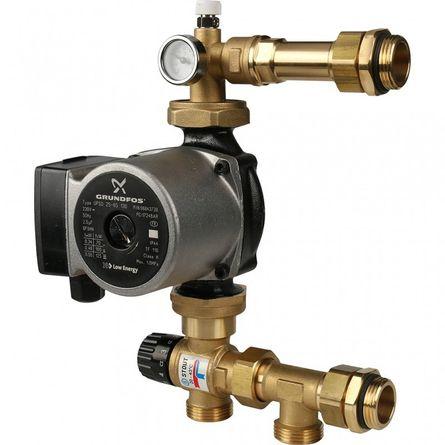

mixing unit
Sometimes it is installed separately, but most often it is present as part of a collector group.
Only the most basic elements are listed. In addition to them, measuring instruments, air vent valves and other additional elements may be present. It is recommended to purchase collectors equipped with security groups. They consist of a drain valve (with a hose fitting) and an automatic air vent. Security groups must be present on both collectors - direct and reverse.
Mixing unit

Produces the preparation of the coolant
One of the most important elements of the manifold group is the mixing unit. It prepares the coolant - it mixes the hot liquid with a colder return. As a rule, too hot coolant comes out of the boiler. In order to maintain the desired temperature, a certain amount of a colder stream is mixed into the incoming liquid.
This process can be organized in two ways:
- with a three-way valve. It is connected to the direct and return lines, and the output is a liquid with the desired temperature. The valve regulates mixing proportions according to a signal from a temperature sensor. Installation with a servo drive is possible, providing full automation of the adjustment process;
- with a two-way valve. The principle of operation is a change in the performance of a direct line, which is mixed with a return line. The lower the pressure, the colder the coolant.
Mixing patterns on a three-way valve are considered more reliable and stable. They work automatically and require only the setting of the desired blending mode. Additional adjustment is made only to change the heating and is carried out in working order.
Manifold installation
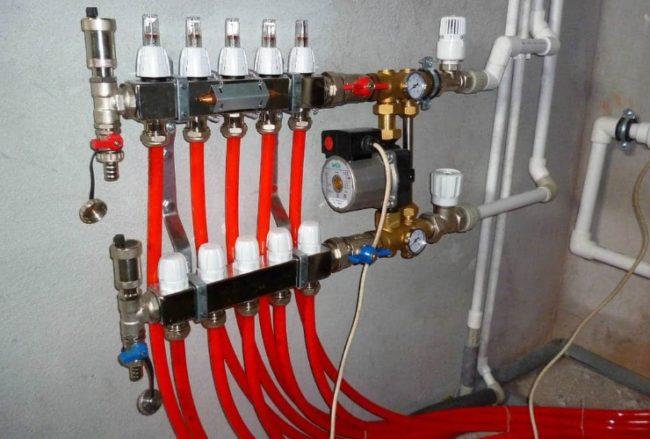

The knot is equipped with two fasteners in the form of metal strips
The collector assembly is installed in a pre-selected location. It is necessary to ensure the minimum length of pipes from the collector to the heat carrier source and to the underfloor heating loops. As a rule, the place for the collector group is chosen during the design process, before the hinges are laid. The procedure for mounting the collector group itself is not particularly difficult - the assembly is equipped with two fasteners in the form of metal strips with holes for screws or nails.
The main part of the work consists in connecting the loops and laying the supply and return pipelines.
In the connection process, you must act slowly, thoughtfully and carefully. The main thing is not to confuse the ends of the loops and connect them to the corresponding outputs of the collector group. All pipelines must be placed in one row, marked by loop numbers and direction of coolant supply.
Frequently asked Questions
Experts recommend choosing devices on three-way valves. They are more efficient, more practical and have a wider range of possibilities. Manifolds on two-way valves are less efficient and may not be used in all systems.
Self-assembly allows you to create a node with individual indicators. You can purchase several collectors and connect them into one cascade. However, to achieve the required quality of work, experience and skills in assembling such circuits are needed. Prefabricated manifold groups are easy to install and require little or no adjustment. However, they have a certain number of outputs, which limits the capabilities of the system.
As a rule, underfloor heating loops are calculated to cover the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe room. Therefore, the presence of emergency exits is impractical - most likely, they will not be in demand. If for some reason it is necessary to assemble additional loops, additional collector sections can be attached.
The most effective option is adjustable valves with servomotors, acting on a signal from a temperature sensor or (better) from a control unit.Manual mode adjustment is used only in regions with a mild and stable climate, where there are no sudden temperature changes and frequent readjustment of the heating mode is not required.
It is strongly recommended to purchase the same collectors for the forward and return lines. This will ensure a uniform circulation of the coolant, will make it possible to use the same connecting elements.