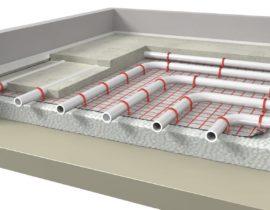
A water heated floor is a pipeline with a heat carrier placed under the floor covering. The implementation of the system is based on the transfer of thermal energy from the coolant to the floor surface, which gives off heat and heats the room. The choice of pipes for underfloor heating is very wide.
The use of one or another option is based on the characteristics of the premises, the installation option and the financial capabilities of the owner of the house. At the same time, saving on the quality of a warm floor is doubtful, since a competently and reliably equipped system serves almost unlimited time, so the costs are one-time, and the service is permanent. Consider the types and features of pipes for underfloor heating water systems more carefully.
Content
What are underfloor heating pipes
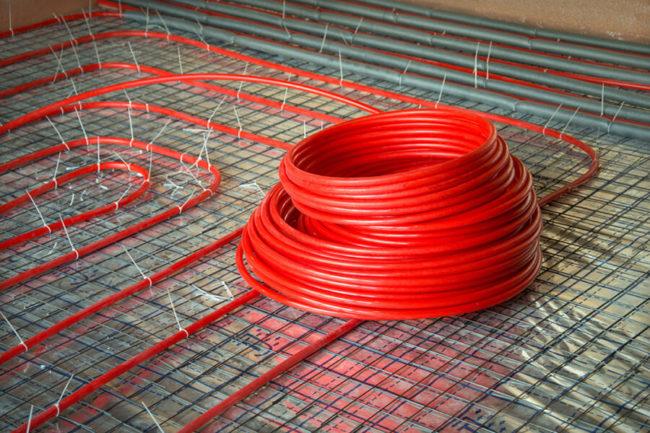

Pipes for water floor heating
Main node water heated floor - this is a complex system of flexible pipelines through which a preheated coolant circulates (usually, it is plain water). The pipes are connected to a manifold group that provides distribution and control of the system operation mode.
Strictly speaking, it is the piping system that is the warm floor in the usual sense.The installation of the circuit is carried out with the calculation of the most uniform arrangement of the turns on the surface of the subfloor. Manufacturers of pipes for a water-heated floor use various materials.
Requirements for the performance properties of water floor heating pipes:
- high heat transfer;
- flexibility, which makes it possible to give the pipes the necessary configuration without destruction;
- durability, strength, invariability of characteristics during the entire service life.
The samples that exist today fully satisfy all user requests and are reliable and efficient pipes for underfloor heating.
Varieties
There are many types of pipelines for underfloor heating. First of all, they differ in the material of manufacture:
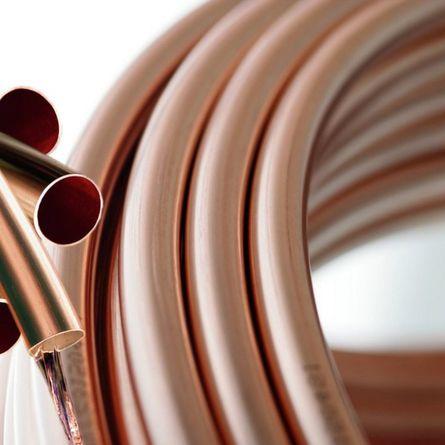

copper
They have excellent heat transfer, the service life is comparable to the service life of the house itself, which allows them to be laid in a concrete screed. At the same time, copper pipes are not plastic, they need to be soldered and are not available for self-assembly (most often). The need to contact specialists for installation, as well as the high price, limit the use of such material;
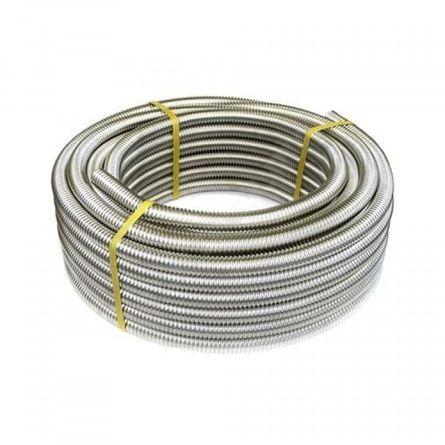

stainless steel
Corrugated stainless steel pipe is new on the market. It can be easily bent by hand, with a minimum bend diameter of only 3 pipe radii, allowing it to be laid in any convenient pattern. Self-assembly is possible without the use of welding. Long service life, excellent performance. In addition, such a material is much cheaper than copper, which promises him very broad prospects;

metal-plastic
The most common material for underfloor heating equipment, available for self-assembly and relatively inexpensive.Usually consists of three main layers: inner and outer - polymer, middle layer - aluminum. They are connected to each other with adhesive layers. Pipes are easy to install, easy to bend, have good working qualities and durability;

PEX
Made from crosslinked polyethylene. Plastic, well transfer thermal energy. They require care during installation, as they can be damaged quite easily. Installation does not require sophisticated equipment, is done manually and is available for independent implementation. The peculiarity of such pipes is that cross-linking is a physico-chemical process that never stops, which is why the finished contours change their parameters over time;

PE-RT
New, made of high temperature resistant polyethylene. High strength combined with flexibility and ductility at low prices create very promising prerequisites for this material. Very easy to install, no special equipment required. Repair work, repeated connection or disconnection without loss of working qualities are allowed;

polypropylene
They have the lowest price, but also the largest bending diameter, which makes them less successful for underfloor heating equipment. It is believed that polypropylene pipes have too low heat transfer, although there are also adherents of PP pipes.
The choice of material is usually made on the basis of the availability of self-assembly, the availability of the material on the market and its cost. It should be noted that saving on underfloor heating pipes, especially when installed in a screed, is undesirable, since the possibility of repairing already filled pipes is extremely low. The service life of a water heated floor system is too long for the savings to make sense.
The shape of the pipe are:
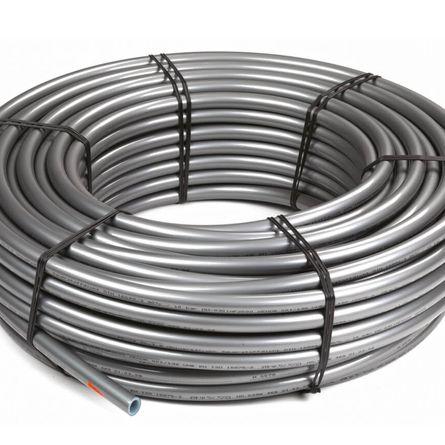

straight
They are produced according to standard technological schemes, bending is carried out due to the material's own elasticity;
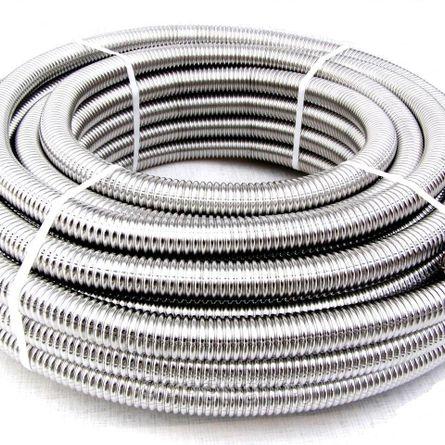

corrugated
Their surface is made in the form of annular waves, which significantly increase the heat transfer area. The bending of such pipes does not create a threat of deformation or destruction, since the plasticity of the material is not involved here.
The diameter of the pipes is one of the basic characteristics of a water heated floor.
The following parameters directly or indirectly depend on it:
- the height of the rise of the level of the warm floor;
- the amount of coolant in the system and the cost of heating it with autonomous power;
- pump performance, power sufficient to overcome the resistance of the system.
Usually, the diameter of a water heated floor is in the range of 16-22 mm. This is quite enough for normal hydraulics and heat transfer to the floor surface.
Features of laying pipes for a water-heated floor
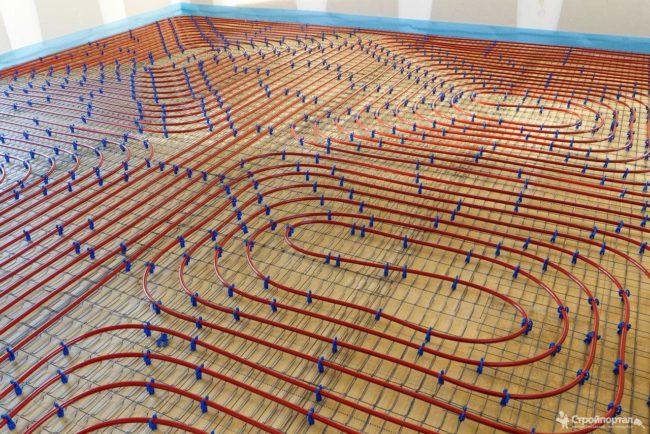
Pipe laying features
Pipes should be distributed on the surface so that they cover the area as evenly as possible, without accumulations in one place and empty spaces in another. The exception is furniture items, for example, cabinets, furniture walls that are planned to be installed in these places - a warm floor is not mounted under them. Also, you can not lay a warm floor under household appliances - for example, refrigerators, stoves, etc.
There are several installation methods:
- spiral;
- snake;
- snail;
- zigzag.
The names of the methods speak for themselves - a certain geometric figure is taken as the basis for the option.At the same time, the following circumstance must be taken into account: pipes under pressure tend to change the given configuration, in other words, they begin to straighten, which disrupts the laying order.
To prevent this from happening, the pipes are fixed on the base in various ways:
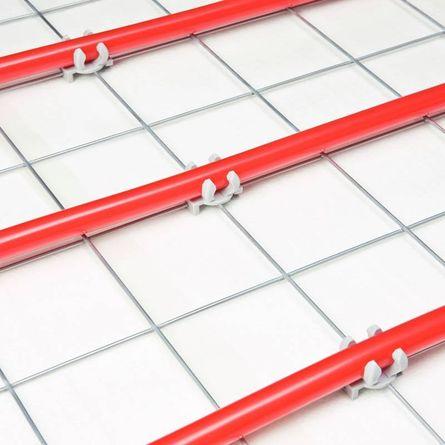
on reinforcing mesh
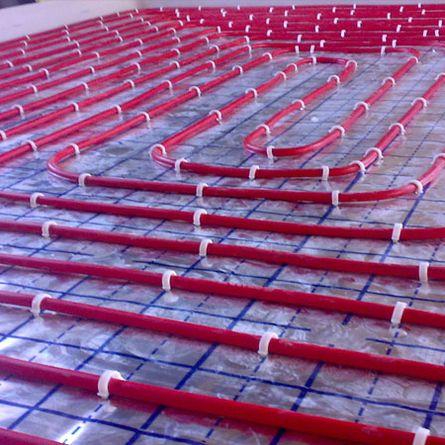

for insulation
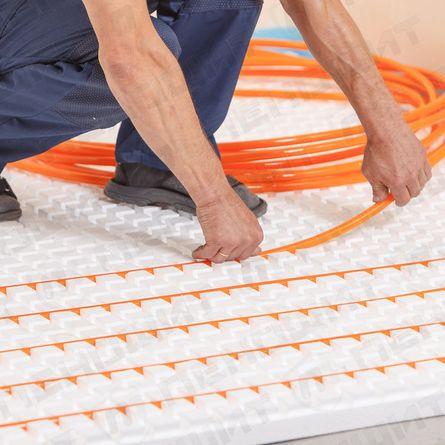

on mats (modular system)
Each pipeline has an inlet and outlet. That is, speaking in familiar plumbing terms, about half the length is a straight line, and the second is a return line. If you lay long loops in the usual way, it turns out that the part that is closer to the entrance is warmer than the one that is close to the return. There is an uneven heating of the room. The way out was double laying, when the loop pipe is folded in half lengthwise and laid according to the scheme.
It turns out that the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe room is evenly distributed between the lines with direct movement, which also correspond evenly with lines with a return. The maximum distance between adjacent sections is 30 cm, the minimum is 10 cm, the layout is usually used in increments of 5 cm - 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 cm.
Contours of a water heated floor

Pipes are divided into groups
Usually pipes do not have a single beginning and end. They are divided into groups (loops, contours). This is done in order to reduce the length of the pipeline, otherwise there will be too much resistance, which will require a powerful pump to overcome. An excessively high pressure will appear in the system, which the pipe material or fittings will not be able to cope with. In addition, with a large length of pipes, they will quickly cool down, which will reduce the efficiency of the system.
Usually, for a small room, one circuit is used, for larger ones, two or more.
The main criterion for the number of loops is to maintain the correct distance between adjacent pipes - about 30 cm maximum (or less, about 15, if more dense heating is required). To combine all circuits into a single system with the ability to control the operating modes of each of them, collector, which can turn off a circuit that is not currently needed while the overall system is running.
Calculation of the contour and pipe consumption
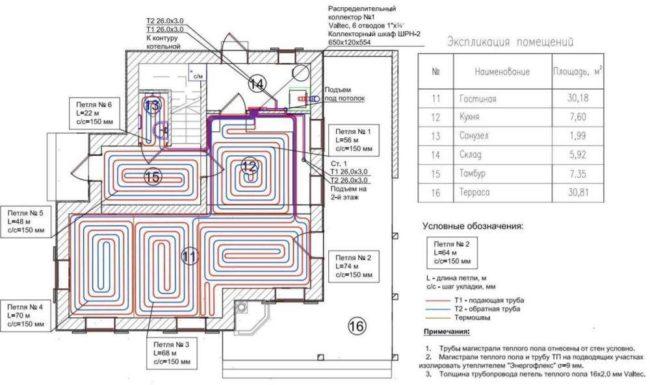
Contour calculation example
A complete calculation of the contour is a difficult task; knowledge of hydraulics, heat engineering and other technical disciplines will be required. A way out of the situation can be an appeal to specialists who have the appropriate training and specialize in calculating warm water floors.
You can do it even easier (and cheaper). There are many online calculators on the network with which anyone can calculate the pipe consumption based on the area of \u200b\u200bthe room.
It should be borne in mind that when calculating the area, it is necessary to take into account only that which will be used for underfloor heating, without areas intended for furniture, appliances, etc.
In addition, it is recommended that when measuring, there is a distance of 20 cm from the walls, which is necessary for the correct operation of the damper tape.
Fittings for water floor heating
Fittings are connecting elements that allow you to securely join pipes to each other or to control elements.
Each type or diameter of pipe has its own fittings, specially produced for this task, although interchangeability of elements is possible, but no one will guarantee the performance of such connections. There are many varieties of fittings both in connection method and material.
By connection method are used:
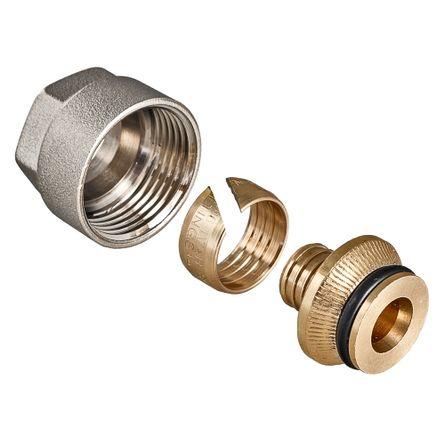

threaded
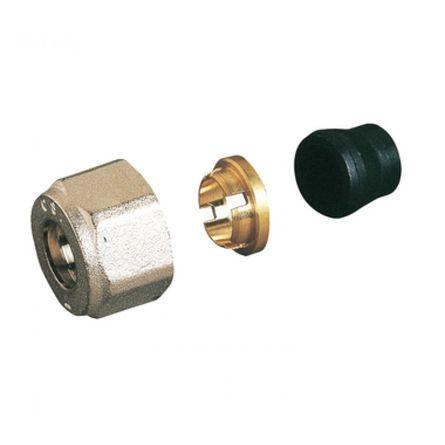

crimp (compression)
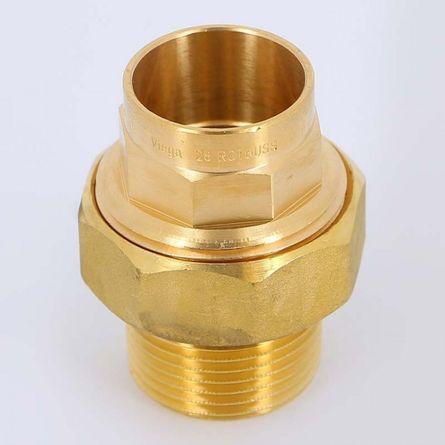

for capillary soldering (used on copper pipes)
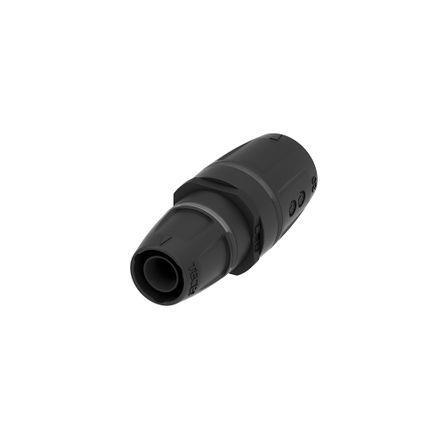

self-locking
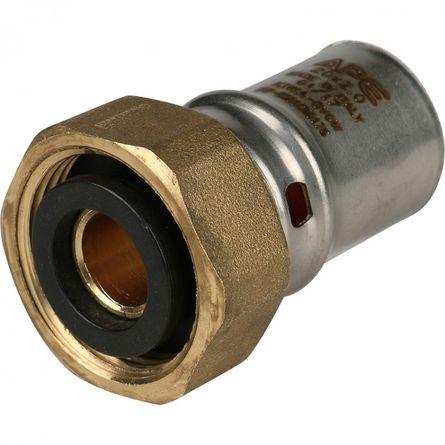

press fittings
Fitting materials are:
- cast iron;
- steel;
- copper;
- bronze;
- polymers - polybutylene, polyvinyl chloride, polypropylene.
For work in underfloor heating systems, mainly compression, self-locking or press fittings are used, which do not require welding equipment, are simple and reliable in operation.
Which pipes to choose?

Which pipes are better to choose
Choosing the most suitable pipes is not an easy task. Here it is necessary to take into account all working moments, from the number of circuits to the operating pressure in the system.
In addition, other factors must be taken into account:
- subfloor material;
- terms of Use;
- parameters of the coolant supply system;
- installation method;
- system load, etc.
Comparing all these factors, they select the most suitable type of pipes and fittings for them. The main selection criterion should be considered the operating pressure in the system. For large values, metal pipes and appropriate fittings are required; polyethylene or polypropylene pipelines are chosen for connection to low-performance sources.
It must be borne in mind that the stronger the pipes, the more difficult the installation and the greater the risk of leakage due to poor quality connections.
However, a system assembled on the basis of polymer pipelines does not tolerate excessive loads and is often damaged when performing various work on the floor surface.
FAQ
It is easier to work with polymer pipes. If straight copper or stainless tubing is used, a large number of fittings will have to be used, which greatly increases labor intensity and increases the number of possible leak points. However, the work spent is not in vain - if the installation is done with high quality, you can no longer worry about the state of the system.
As a rule, this point is already taken into account in the calculation process. However, you can additionally give a little margin of length when installing from the manifold to the entrance to the screed (or under the sheeting).
Basically, you can. However, all loops will have different indicators for hydraulic resistance and allowable loads. If power is supplied from a single source, you will need to install your own collector group for each type of pipe. These points must be taken into account when setting the operating mode.
In the formulas for calculating the diameter of pipes, the internal diameter is searched. Some pipes (for example, metal-plastic) have a large wall thickness, which gives a large error when using the outer size. In addition, the performance is determined by the inner diameter.Therefore, it is more correct to be guided by the inner diameter - it is relevant regardless of the material.
A large number of sharp turns increases the hydraulic resistance of the coolant. This means that for metal pipes that are assembled on brazed fittings, a more powerful circulation pump is needed.