The underfloor heating system is the best option for heating in a private house. It is very economical and may well be powered by its own boiler, which makes the house almost autonomous, independent of the appetites of resource supplier companies. At the same time, the installation technology and the overall calculation of the system become an important point.
These are the two main points on which the durability and efficiency of the system depends. If you can use an online calculator for the calculation, and for a more correct result, the procedure can be easily duplicated on other resources, then the installation is carried out independently. A water heated floor does not allow mistakes or a frivolous approach - leaks appear that require an immediate shutdown of a section of the system and complex and expensive repairs.
Content
Features of the design of a water heated floor

Water heated floor in a private house
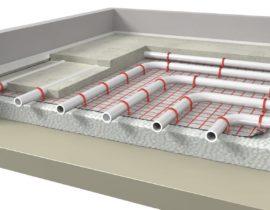
The water heat-insulated floor represents the system of heating of rooms distributed on all their area. From the point of view of design, this is a conventional pipeline into which a coolant (hot water) is supplied. This is the main difference between electrical and water systems - the former themselves generate thermal energy, the latter receive it from the outside and only distribute it over the floor surface.
The main feature of a water-heated floor is the uneven heating of the tube. The coolant enters it and, passing along the entire length, gives off thermal energy, cools down. This is the practical difference between a water system and an electric one - a heating cable or a film floor at all points gives the same degree of heating.
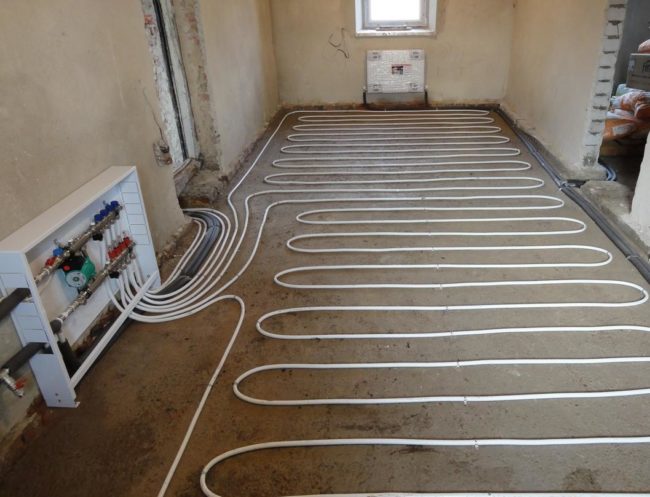 For more uniform heat transfer, the water heated floor is divided into segments - loops. This allows you to significantly reduce the loss of thermal energy - the temperature drop when passing 10 m is much less than when passing 100 m (dimensions are given as an example).
For more uniform heat transfer, the water heated floor is divided into segments - loops. This allows you to significantly reduce the loss of thermal energy - the temperature drop when passing 10 m is much less than when passing 100 m (dimensions are given as an example).
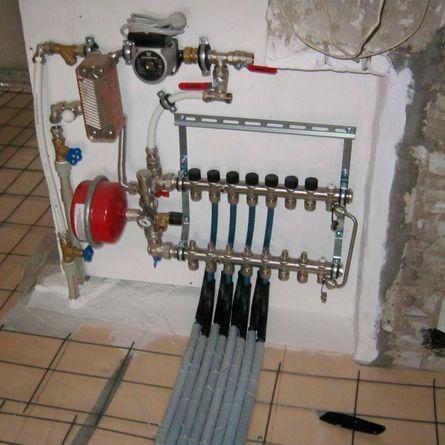
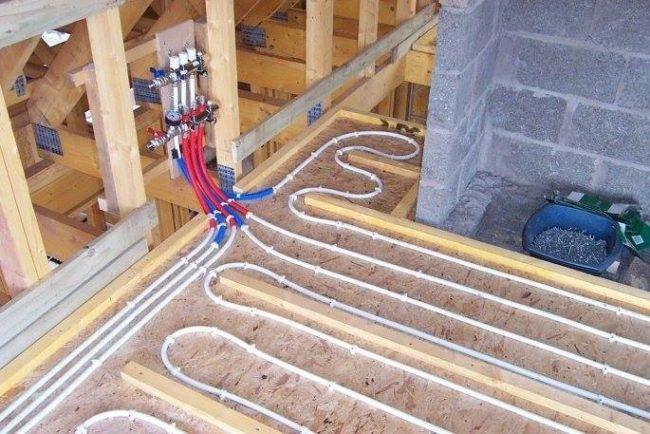
Each loop is connected to its own coolant supply point, and also to its own return line. For this, two collectors are used - one distributes the hot coolant of a straight line along each loop, and the second receives the cooled water and directs it to heating.
Collector allows you to turn off each loop, or re-supply coolant into it. This is very convenient, since in each room you can create your own heating mode, and when not in use, do not waste fuel and resources on unclaimed work. Considering that such possibilities arise when the collector is fed from a single pipe, the advantages of such systems become obvious.
Another feature of the water floor heating should be considered the temperature regime. The maximum temperature of the coolant in the system is 55 ° C, and the normal temperature is 40-45 ° C (the temperature regime depends on the installation method and is quite easily regulated).
Therefore, to set the temperature in the system, a special device is used - a mixing unit.In it, the hot coolant in a certain proportion is connected to the cooled flow from the return line, giving out a liquid with a given temperature at the outlet. This allows you to fine-tune the heating, unlike electrical systems, where the adjustment is stepwise (2-3 positions).
Possible sources of coolant
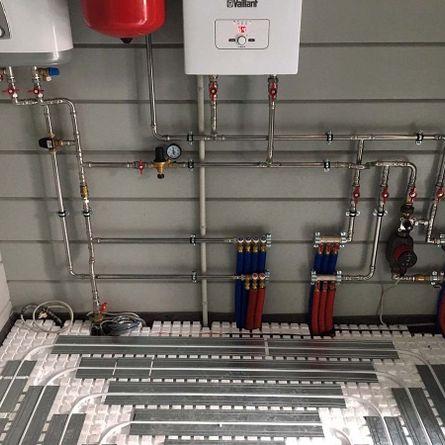


The source of the heat carrier can be the central heating system or your own boiler. In the first case, there is a significant advantage - there is no need to prepare hot water on your own. However, the cost of resources and the need to obey the heat supply regime make this option not the most convenient and cheap.
In addition, the supply of a warm floor from the central heating network is a very delicate and controversial issue, the solution of which can be either positive or negative. Officials from licensing authorities are used to insuring themselves, and in doubtful situations, just in case, they refuse permission. As a rule, owners connect underfloor heating to the central heating system at their own risk, which one day can create considerable problems.
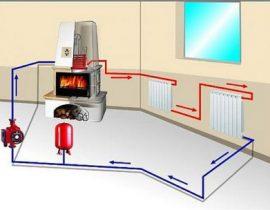
Powering the system from its own boiler does not create any administrative problems. Water is heated and enters the supply tank (boiler storage), from where it is supplied to the system, goes through a circulation cycle and returns to the same boiler for heating. From the point of view of economy, this option is the most effective - all costs are expressed in the cost of fuel needed to heat water. If a gas boiler is used, all system operation takes place automatically and does not require constant attention.
Among the advantages of powering a warm floor from your own boiler are:
- the beginning and end of the heating season does not depend on the heat carrier supply schedules;
- the ability to independently regulate the operating mode and temperature of the coolant, which will allow fuel consumption with maximum rationality;
- it is always possible to install an additional heater, or replace the boiler with a more powerful model, which will allow you to optimally adjust the operating mode of the system.
The only drawback can be considered the dependence of heating on the state of the boiler and the availability of fuel. However, here you can play it safe and use a combined boiler (capable of operating on different types of fuel, for example, gas-wood).
Hinge mounting methods
Underfloor heating loops are the executive body of the system, providing a uniform supply of heat. At the same time, the overall heating efficiency depends on the method of installation and laying of the loops.
There are two main options:
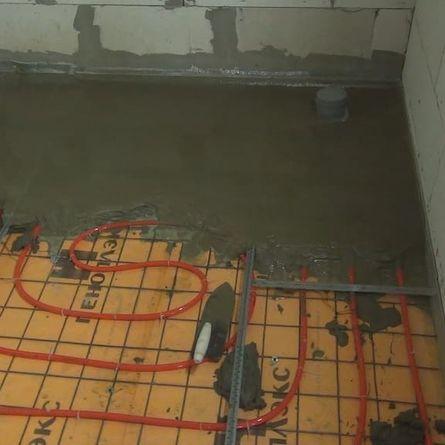

laying hinges in a concrete screed
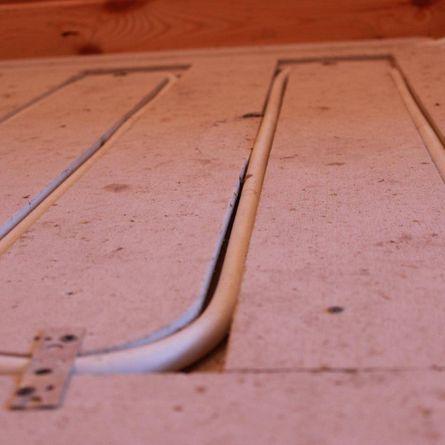

laying the system on a wooden or polymer base without pouring with hardening compounds
Pouring pipes into a screed is the most effective option in terms of heat transfer. In this case, there are practically no heat losses, all thermal energy is transferred to the screed, which acts as a buffer radiator. The screed has significant inertia; when the coolant is turned off, it will not cool down immediately. If it is necessary to carry out any work on the boiler, a short break will not be noticeable. In addition, the screed can be laid ceramic tiles or porcelain stoneware - walking barefoot on such a floor is very pleasant.
The disadvantage of this method is the complexity of the repair work.If a leak appears, you will have to break the screed and change the loop, which requires considerable effort and expense. Even detecting a leak is not easy if it is not above the basement - the floor covering can hide the wet spot and not show the problem in any way.
It is quite easy to damage the pipes if a hole is drilled on the floor for fasteners - a polyethylene (or polypropylene) pipe with a diameter of 16-20 mm is used during assembly. It is quite difficult to get into it with a drill, but the probability of an undesirable event is always greater (Murphy's law, or, in common parlance, the law of meanness),
 Laying loops on wooden base - Easier and faster installation. The pipes are laid on a wooden flooring made of boards or sheet materials, covered with a waterproofing film (membrane).
Laying loops on wooden base - Easier and faster installation. The pipes are laid on a wooden flooring made of boards or sheet materials, covered with a waterproofing film (membrane).
To fix the position of the pipes, a heat insulator is used. You can choose mineral wool or penoplex, often ordinary wooden planks are used, between which pipes are laid. This option is the simplest and most effective.
The disadvantage of this design is the low efficiency of heat transfer (in comparison with the screed).
However, there are also advantages:
- the absence of "wet" work, threatening leaks and damage to the decoration of the premises below the floor;
- high laying speed;
- there is no need to wait until the screed hardens;
- high maintainability - if necessary, you can easily remove the flooring, dismantle the flooring and gain access to the pipes. At the same time, repairs can be completed in one day (if there is a point problem).
These advantages for many homeowners become quite strong arguments that determine the choice of installation method.
Pipe laying
The uniformity and efficiency of the warm floor depends on the configuration of the pipeline. Each loop is responsible for heating a specific area of the surface. It can be one small room entirely, or part of a larger room. The pipe must be laid so that the heat transfer from each of its sections is as efficient as possible.
Different ways (schemes) of laying are used:
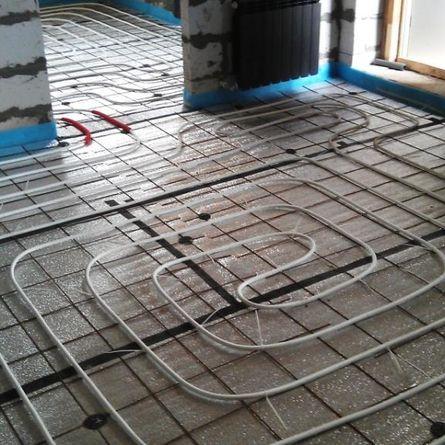

spiral
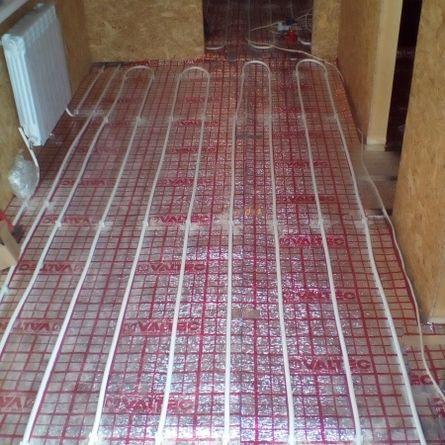

snake straight and angled
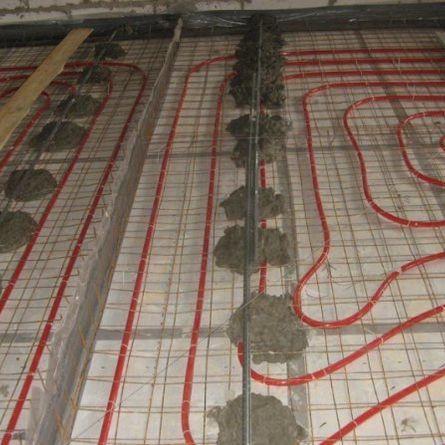

zigzag
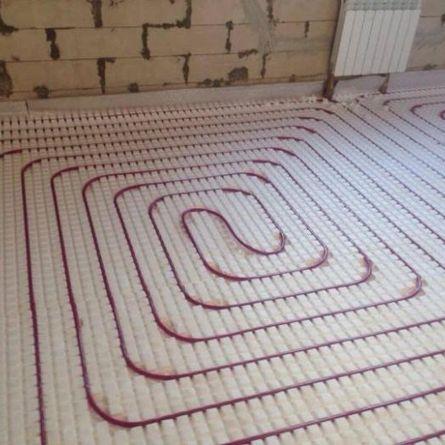

snail
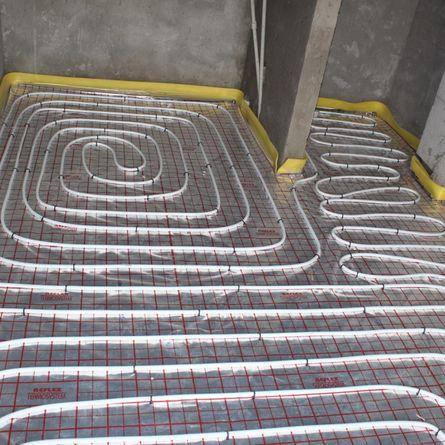

combined scheme
In addition, for each scheme, there are single and double laying options. In the first case, the pipe is completely laid in a certain way, in the second it is first folded in half, after which it is laid according to the chosen scheme. It is believed that the double option contributes to less cooling of the coolant and increases the efficiency of the system.
The choice of one or another option depends on various factors:
- the size and configuration of the room;
- allowable pipe bending radius;
- distance to the collector.
In addition, an important indicator is the pitch of the pipes. This is the distance between adjacent turns. It must be chosen so that the pipes do not cool too much (this happens if the pitch is too large), but they are not too tightly laid (due to this, material consumption and the length of the loops increase).
Questions
If the source of the heating medium is your own boiler, no permits are required. However, if it is planned to connect to the DH system, it is better to obtain permission. At the same time, it must be borne in mind that if officials decide to play it safe and refuse to issue a permit, you will have to do the installation at your own peril and risk.At the same time, an administrative check of the design of the heating system is possible with undesirable consequences.
This is an undesirable option, since you will have to balance the load and adjust the temperature on each circuit. It is recommended to stick to the same length of all contours, although in practice this is not always possible.
The limit value is 100 m. However, for more economical and efficient operation of the system, a shorter length is chosen - 80 m. This applies to polyethylene and polypropylene pipes with a diameter of 16 mm. If the pipe diameter is larger, the allowable length increases. For example, for 18 mm pipes, the limit value will be 120 m.
As a rule, their own circulation pump is used for underfloor heating. It is installed in a manifold cabinet. This allows you to remove excess load from the boiler, stabilize the operation of the underfloor heating and provide more even pressure in all circuits.
Here the criterion is the size and shape of the room. for small narrow rooms choose a zigzag or snake, for larger rooms - a spiral, a snail or a combined styling option. It is also necessary to pay attention to the pitch of the pipes and the distance between the loops - if a large gap is obtained, the floor surface becomes unevenly heated. This is felt when walking barefoot and reduces the level of comfort.